Many custom options...
And formats...

Not what you want?
Try other similar-meaning words, fewer words, or just one word.
U R Still in Chinese / Japanese...
Buy an U R Still calligraphy wall scroll here!
Personalize your custom “U R Still” project by clicking the button next to your favorite “U R Still” title below...
1. Do not fear being slow, fear standing still
4. Faith is the bird that feels the light when the dawn is still dark
6. Inner Peace / Silence / Serenity
9. Guo
10. Even The 100-Foot Bamboo Can Grow One More Foot
11. Dragon Warrior
12. Palestine
13. Stay Strong / Indestructible / Unbreakable
15. Warrior Saint / Saint of War
16. Peaceful / Tranquil / Calm / Free From Worry
17. Distance Runner
18. Shang
21. The Sea of Knowledge Has No Limits
23. Jew / Jewish
24. Persistence
25. Selflessness
26. Sacrifice
27. Sparrow
29. Secret
30. A Deliberate Inaction is Better than a Blind Action
31. Manga
33. Kindheartedness / Benevolence / Humanity
35. Sakasa / Reverse
37. Ritsu
39. Tranquility Yields Transcendence
43. Body
45. Xing Yi Quan
48. A Journey of 1000 Miles Feels Like One
49. Chinese or Korean Army General
50. Even a fool may sometimes come up with a good idea
51. Boxing
52. Banzai
53. Pain
54. My True Love
55. Caring
56. Everything Happens for a Reason
57. Bonsai / Penzai
58. Flowers / Blooming / Splendid / China
59. Ice / Frost
60. Prosperity
61. Cuong Nhu
62. Better to be Happy than Rich
63. Goddess of Mercy and Compassion
64. Law of the Fist Karate / Kempo Karate
65. Life Energy / Spiritual Energy
66. Honor
67. Devotion / Dedication / Attentive / Focused
68. Sword
70. Confucius
71. Banzai / Wansui
72. Drain the pond to get all the fish
74. A sly rabbit has three openings to its den
75. Gung Ho
77. Reiki
Do not fear being slow, fear standing still
Calm / Tranquility
安 is used in a lot of compound words in the CJK world.
Alone, this character has a broad span of possible meanings. These meanings include relaxed, quiet, rested, contented, calm, still, to pacify, peaceful, at peace, soothing, or soothed.
安 and even the pronunciation was borrowed from Chinese and absorbed into both Japanese Kanji and Korean Hanja. In all these languages, this character is pronounced like “an.”
Silent / Solitary
寂 means silent, solitary, quiet, calm, still, rest, or tranquil.
This also has a strong association with Buddhism where it can mean “entering into Nirvana.” In that context, this is sometimes used to refer to the passing of a Buddhist monk (he is silent, as he has entered Nirvana). For the living, this is about tranquility (especially of mind).
Some will also use this to mean “elegant simplicity.”
From Sanskrit, this can represent praśama, vivikta, śānti, or nibbāna (nirvāṇa).
Faith is the bird that feels the light when the dawn is still dark
信唸是在黎明前的黑闇中能感到光明的鳥 is a philosophical poem/quote from Indian Poet and Philosopher, Rabindranath Tagore.

Rabindranath Tagore, 1915
This quote is not sourced, and therefore several variations exist in English. Some suggest the original was in the Bengali language.
This, of course, is the Chinese translation that has the meaning of, “Faith is the bird that feels the light and sings when the dawn is still dark.”
More about Rabindranath Tagore
Serenity / Tranquility
Inner Peace / Silence / Serenity
靜 is the simplest way to convey the meaning of inner peace and serenity.
靜 is often translated as “serenity.” It can also be used to express the ideas of still, calm, serene, quiet, silent, stillness, not moving, or tranquility.
In the old days, Chinese, Japanese, or Korean people might hang a wall scroll with this character in their reading room to bring about a sense of peace in the room.
![]() While they once used the same character form in Japan, they now use a slightly-simplified version in modern Japan (after WWII). This version is shown to the right, and can be selected for your wall scroll by clicking on that Kanji instead of the button above.
While they once used the same character form in Japan, they now use a slightly-simplified version in modern Japan (after WWII). This version is shown to the right, and can be selected for your wall scroll by clicking on that Kanji instead of the button above.
See Also: Peace
Indomitable Spirit
Korean Only
百折不屈 is a Korean proverb that means “indomitable spirit,” at least, that is the way it is commonly translated in martial arts circles (Taekwondo, Hapkido, etc.).
The literal translation is “[one] hundred [times] broken [still] don't succumb.”
Or more naturally translated, “Even if attacked/beaten one hundred times, still be undaunted/indomitable.”
Notes:
Some will say this is one long word rather than a proverb.
This is also a proverb/word in Chinese though rarely used in modern times.
Sasuga / Nagare
Guo
Surname
Even The 100-Foot Bamboo Can Grow One More Foot
Dragon Warrior
Palestine
Stay Strong / Indestructible / Unbreakable
金剛不壞 is originally a Buddhist term for “The diamond indestructible.”
Sometimes, it's written 金剛不壞身, The diamond-indestructible body.
Outside that context, it still means firm and solid, sturdy and indestructible, unshakable, or adamantine (a mythological indestructible material).
![]() Note: If you order this from the Japanese master calligrapher, the last Kanji will look like the one shown to the right.
Note: If you order this from the Japanese master calligrapher, the last Kanji will look like the one shown to the right.
Always Try to do Better
This Japanese proverb literally translates as: [After having achieved a fair degree of success,] one should still try to do better.
Others may translate this as “Always try to improve,” or “Always try to be better.”
Note: Because this selection contains some special Japanese Hiragana characters, it should be written by a Japanese calligrapher.
See Also: Never Give Up
Warrior Saint / Saint of War
Peaceful / Tranquil / Calm / Free From Worry
This is a nice word that means peaceful, tranquil, calm, composed, “free from worry,” “public peace,” tranquility, good health, well-being, or welfare in Chinese and Korean.
Note: The definition in Japanese is not so broad but still means peaceful or “public peace.”
Distance Runner
Shang
Surname
This is the most common character for the Chinese surname that romanizes as Shang. This is also a name, “Makato” in Japanese and “Sang” in Korean.
尚 is also a word meaning: still; yet; to value; to esteem; furthermore; in addition; greater; further.
Naginata / Halberd
Drink Up! / Cheers!
Alternate version
The Sea of Knowledge Has No Limits
學海無涯 is a Chinese proverb that reads, “sea of learning, no horizon.”
Colloquially, it means there are no limits to what one still has left to learn.
This would be the Chinese equivalent to the quote from Hippocrates, “ars longa, vita brevis,” meaning “it takes a long time to acquire and perfect one's expertise.”
See Also: Learning is Eternal
Serenity / Tranquility
靜穏 is a Japanese-specific way to express “serenity” or “tranquility.”
Notes: The second Kanji is not a Chinese character - it was morphed or developed in Japan after Chinese characters were absorbed into the Japanese language during the 5th century.
The first character is slightly-simplified from the original Chinese form but still recognizable.
See Also: Peace
Jew / Jewish
猶太 is the title for Jews or the adjective for being Jewish in Chinese.
You may be surprised to learn there are still a few native Jews in China (though many ethnic Jews moved to Israel). It's believed that they are descendants of traders who traveled the silk road between the Middle East and the Orient.
Persistence
固執 can also mean “opinionated” or “stubborn” in Chinese and Japanese, but in the nicest way possible (still bad).
This just means “stubborn” in Korean (not a good scroll if your audience is Korean, in fact, we don't recommend this word at all). There are better ways to express this idea, such as tenacity/tenacious or perseverance... ...see the links below...
See Also: Tenacious | Fortitude | Perseverance
Selflessness
無私 would be literally translated as “none self” in Chinese, Korean, and Japanese.
It is used to express “selflessness” or “unselfish.”
無私 is a popular term for the idea of being selfless or unselfish in modern China and Japan.
This term is not as commonly used in Korea but still has good meaning.
Sacrifice
犧牲 means sacrifice in Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and old Korean Hanja.
There is a suggestion in this word that this regards sacrificing your life.
Note: Depending on the context, this can also mean victim or scapegoat in Japanese.
In original and ancient Chinese, this word referred to sacrificial animals. It can still have this meaning in a Buddhist context.
![]() The version of the first character used in modern Japan looks like the image to the right. If you order this from the Japanese master calligrapher, it will be written in this Japanese version.
The version of the first character used in modern Japan looks like the image to the right. If you order this from the Japanese master calligrapher, it will be written in this Japanese version.
Sparrow
麻雀 is the common and specific name for a hemp sparrow bird in Chinese.
This was also the original name for the game, known commonly as Mahjong. You will still see boxes of Mahjong tiles with the title 麻雀 for sparrow instead of the modern 麻將 in Southern China. This title is also used for Mahjong in Japan.
Sit Quietly in Meditation
A state of mind
入靜 is used in Taoism and Qi Gong to describe the state you can reach while sitting quietly in meditation. It contains the idea of achieving a highly-tranquil and peaceful state. Some may describe this state as “sleeping while still awake.”
If you have a relaxation or meditation room, this is the calming wall scroll that you would want hanging in that room.
Secret
密 can mean secret, secrecy, confidential, quiet, still, and/or esoteric.
As a piece of calligraphy artwork, it will be read with this secret or secrecy meaning.
When used in the context between people, this can mean: close; close together; intimate; closed in.
When referring to materials or objects, it can refer to thickness, density, thick, dense, fine, and/or small.
Notes:
In Chinese, this can be the surname Mi.
In Japanese, this can be the name Mitsu.
A Deliberate Inaction is Better than a Blind Action
Sometimes 一動不如一靜 is translated by others as “Look before you leap” but the more accurate and direct translation is the one I used in the title.
While somewhat military in its origin, this proverb can apply to any situation where a decision needs to be made, but perhaps there are still some “unknowns.”
This phrase suggests that in our “action-based” world, sometimes the “smarter move” is “no move at all.”
See Also: Better to Choose Nothing Rather Than Make a Poor Choice
Manga
漫画 is the Japanese word for cartoon, comic, caricature, or comic strip.
The older traditional form is 漫畫 and is sometimes still used in Taiwan and China (and occasionally in Japan) when referring specifically to Japanese comics.
You'll see the same 漫画 used in Mainland China as well since 画 is not just the modern Japanese form but also the Simplified Chinese version of the original 畫.
Great Expectations
望 holds the ideas of ambition, hope, desire, aspiring to, expectations, looking towards, to gaze (into the distance), and in some contexts, full moon rising.
望 is one of those single characters that is vague but in that vagueness, it also means many things.
望 is a whole word in Chinese and old Korean but is seldom seen alone in Japanese. Still, it holds the meanings noted above in all three languages.
Kindheartedness / Benevolence / Humanity
仁德 is a word that can be translated as love, kindheartedness, benevolence, and humanity.
The first character means benevolence by itself.
The second character means virtue or morality.
Japanese note: The second Kanji of this word has been slightly simplified (one tiny horizontal stroke removed). It is still readable for Japanese but if you select our Japanese calligrapher, expect that stroke to be missing on your wall scroll.
Learning is Eternal
This Chinese philosophy tells of how we continue to learn throughout our lives.
This proverb can be translated in a few ways such as “Study has no end,” “Knowledge is infinite,” “No end to learning,” “There's always something new to study,” or “You live and learn.”
The deeper meaning: Even when we finish school we are still students of the world gaining more knowledge from our surroundings with each passing day.
See Also: An Open Book Benefits Your Mind | Wisdom | Learn From Wisdom
Sakasa / Reverse
逆さ is a Japanese word that means reverse, inversion, upside down, inverted, reverse, opposite, and in some contexts (especially without the secondary hiragana character), can mean wicked.
逆さ has some significance to those practicing certain forms of Japanese martial arts.
Note: The first character is kanji (originally a Chinese character now used in Japanese) it still holds the same meaning in Chinese. However, the secondary hiragana makes this a Japanese-only entry.
Great Lord / Tycoon
大君 is the Japanese word Taikun. It's defined directly as liege, lord, or an alternate title for a shogunate.
The sound of this Japanese word entered the English lexicon by the 1800s but took the spelling of “tycoon.” Even President Lincoln was referred to as a Tycoon in the 1860s.
In Japan, this is still understood as “Great Lord” or “Big Boss.” In America, it means “Bill Gates” and “Warren Buffet.”
Ritsu
While this character literally means law, regulation or rules, it's also a surname Lü in Chinese and name Ritsu in Japanese.
In more ancient times (and for some people still), this can refer to East Asian criminal code, or vinaya (rules for the monastic community). For Japanese Buddhists, this can be the Ritsu school.
In some context, this can refer to certain musical scales used in Asia.
Ichi-Dan / First Degree
In Japanese martial arts, this usually represents the first-degree black belt rank.
It can also be like a linguistic stair step of “more, much more, still more, all the more.” It can also be a step, rung, level, or rank.
Also sometimes used in the context of Buddhism to mean “first step” or “first stage.” This might presume the first step towards enlightenment etc.
Tranquility Yields Transcendence
寧靜致遠 is an ancient Chinese idiom that means “tranquility yields transcendence.”
This suggests pursuing a quiet life of profound study.
The first two characters mean tranquility. The last two characters mean “go far,” which suggests achieving much in your life or expanding beyond normal limits. The direct translation would read something like, “[With] tranquility [in your life, you'll] go far.”
Compare this to the English idiom: Still waters run deep.
Goddess of Compassion
観音 is the specifically Japanese version of Bodhisattva of Compassion or Guan Yin.
In Japanese, this is pronounced Kannon and occasionally spelled Kwannon. The Chinese version is a bit more commonly seen in Asia. However, in Japanese, there is a slight variation with the first character.
Some time ago, a camera company in Japan named their company after this Buddhist deity. That camera company is still known as Canon (they chose a “C” instead of a “K” when they Romanized this name).
Kingdom of Heaven
天国 is the same meaning and pronunciation as our other entry for “Kingdom of Heaven,” but the second character was simplified in Japan and mainland China to this version.
Choose the appearance that you like best (they will be somewhat universally understood - as most people are aware of this simplification in places where they still use all traditional characters - such as Taiwan and Hong Kong). You can consider the other version to be the “ancient version.”
Strong and Beautiful
We don't really have a word like 健美 in English, but these two characters create a word that means “strong and beautiful.” It could also be translated as “healthy and beautiful.”
Note: 健美 is a word in Chinese and Korean, but it's also the family name Takemi in Japanese. The characters hold the same meaning in Japanese; however, it's like having the English name Stillwell when few people would perceive the meanings of still and well.
Body
身 is how to write “body” as in your human body, in Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and Korean Hanja.
Depending on the context and certain language issues, this character can also mean: main part, hull, oneself, somebody, person, I, me, sword, lifetime, one's station in life, etc.
While this written word is universal in three languages, it still makes a rather odd selection for a wall scroll. Also, they tend to use 体 (karada) in Japanese for the body (depending on context).
See Also: Karada
Dragon / Emperor Symbol
竜 is an alternate form of the dragon.
Still pronounced the same in Chinese, Japanese, and Korean.
This particular Kanji is often associated as an imperial symbol as well as representing the mythical Asian dragon. You may have seen it on the chest or flag of the emperor in old Japanese and Chinese movies.
Note: I would rate this as a non-universal alternate form. The other dragon character is by far more common, and universally understood.
We strongly recommend ![]() if you are looking for the symbol of dragon.
if you are looking for the symbol of dragon.
Xing Yi Quan
Style of Martial Arts
形意拳 is the title for the Xingyiquan style/form of Chinese martial arts involving explosive linear movements.
Some translate this as “shape-of-the-mind fist.”
While pronunciation has never changed in Chinese, the old romanization was “Hsing I Chuan.” This romanization for 形意拳 is still used in Taiwan.
This term is used in some Japanese martial arts circles where it's romanized from Japanese as keīken, keiiken, or keiken.
Brief and to the Point
Speak simply, while expressing your idea completely
言簡意賅 is a Chinese proverb that suggests it is better to be brief and use fewer words while still expressing your main point or idea.
In another way to explain this, one should not use 100 words when 50 will do, or being more concise with your speech.
This can also be translated as concise, compendious, “brief in form but comprehensive in scope” or succinct.
This is a bit more positive than our other proverb for brevity.
Guan Gong / Warrior Saint
關公 is a Chinese title, Guan Gong, that means Lord Guan (The warrior saint of ancient China).
 While his real name was Guan Yu / 關羽, he is commonly known by the title of Guan Gong (關公).
While his real name was Guan Yu / 關羽, he is commonly known by the title of Guan Gong (關公).
Some Chinese soldiers still pray to Guan Gong for protection. They would especially do this before going into battle. Statues of Guan Gong are seen throughout China.
A Journey of 1000 Miles Feels Like One
千里も一里 is a Japanese proverb that states “A journey of a thousand miles feels like only one mile.” It is understood that in the proverb, this applies when going to see the one you love.
Note that the “mile” or 里 used in this proverb is an old Chinese “li” (pronounced “ri” in Japanese). It's not actually a mile, as the measurement is really closer to 500 meters (it would take 3 of these to get close to a western mile). Still, 1000里 (333 miles) is a long way.
Chinese or Korean Army General
將軍 is the more Chinese and Korean Hanja version or General.
There is a slight variation in the way the first character is written compared to the Japanese Shogun (将軍) title.
So if you want to specifically refer to a Chinese or Korean General, this is the way. Japanese people would still easily identify this as “shogun.”
Note: This term is also used for Admiral in Korean in a certain context (if you need a better title for Admiral, just let me know).
Even a fool may sometimes come up with a good idea
千慮一得 means “1000 tries, one success,” or “[a] thousand tries [leads to] one success.”
This proverb is a humble way to express your success, ideas, or accomplishments. As if you are a fool who just got lucky in inventing or creating something.
Translations for this proverb include:
Even without any notable ability on my part, I may still get it right sometimes by good luck.
Even a fool may sometimes come up with a good idea.
Compare this to the English idiom, “Even a broken clock is right twice a day.”
Boxing
拳闘 is the term used in Japanese Kanji to refer to the original Olympic sport of combat and fighting.
This can also be translated as prizefighting.
The first Kanji means fist. The second means fight. So when literally translated, this means “fistfight” (though understood in Japanese as a more refined sport, versus street fighting).
Note: A completely different second character is used in the Chinese word for boxing but a Chinese person would still be able to guess the meaning of these Kanji.
Banzai
Modern Japanese Version
万歲 is the modern Japanese way to write banzai.
We've made two almost identical entries for this word, with just a variation on the first character. In the last century, 萬 was simplified to 万 in Japan and China. The new generation will expect it to be written as 万 but the old generation can still read the more traditional 萬 form. You must make your determination as to what version is best for you. If your audience is mostly Japanese, I suggest 万歲.
While it has become a popular, if not an odd, thing to scream as you jump out of an airplane (preferably with a parachute attached), banzai is actually a very old Asian way to say “hooray.” The Japanese word “banzai” comes from the Chinese word “wan sui” which means “The age of 10,000 years.” It is actually a wish that the Emperor or the Empire live that long.
Imagine long ago when the Emperor made a rare public appearance. This is what all of the people would yell to their leader in respect.
So if you like it as a hooray, or you want to wish someone that they live for 10,000 years, this is the calligraphy for you.
To other things with banzai in their names, I am still waiting for the promised sequel to Buckaroo Banzai.
Other translations: hurrah, long life, congratulations, cheers, live long.
Notes: Sometimes people confuse banzai with bonsai. A bonsai is a miniature tree. They have nothing to do with each other. Further, Bonzai is not a word at all - although it would make a great name for a calcium supplement for older people.
Pain
ache / sorrow
痛 means pain in Chinese and old Korean Hanja. It also means pain/hurt/bruise in Japanese but is seldom seen as a single Kanji (usually, at least a Hiragana is added to make the word “itai” which is what a Japanese person will scream when they are in pain).
Depending on the context, this word can mean hurt, ache, sorrow, or refer to damage to a human body. As a single character, the possible meanings are very open - so you can decide what it means to you, as long as the general meaning is still “painful.”
See Also: Hurt
My True Love
我心真愛 is a slightly poetic way to express this sentiment to someone.
The meaning is “My True Love,” but the characters directly translate as “I/Me/My Heart/Mind True/Real Love.”
Note that Chinese grammar and construction are different, so this sounds very eloquent and artsy in Chinese.
In Korean Hanja, the third character should be written differently. Just let me know when you place your order if you want that version - it will still make sense in Chinese. This phrase makes sense in Korean but is not commonly used.
Caring
關心 means caring in Chinese.
Caring is giving love and attention to people and things that matter to you and anyone who needs help. When you care about people, you help them. You do a careful job, giving your very best effort. You treat people and things gently and respectfully. Caring makes the world a safer place.
Note: 關心 is also a word in Korean Hanja, but in Korean, it means taking interest or concern. In Korean, it's still a good word, but it doesn't quite have the “caring for a person” meaning that it does in Chinese.
See Also: Benevolence | Altruism
Everything Happens for a Reason
物事は全て理由があって起きる means everything happens for a reason.
However, this is a work in progress. We're still trying to decide the best way to express this in Japanese. If you order this, we might have a discussion about the best version that fits you. Here's how the characters break down by meaning (keep in mind, Japanese grammar and sentence construction is very different from English, so it doesn't make complete sense in English)...
物事 = things, everything
は particle
全て all, the whole, entirely
理由 reason
が particle
あっ be, exist, have, take place, happens
て particle
起きる to occur, to happen; to take place (usually unfavorable incidents)
Note: Because this selection contains some special Japanese Hiragana characters, it should be written by a Japanese calligrapher.
Bonsai / Penzai
Dwarf Tree Culture
盆栽 is the word that refers to the culture, hobby, and to miniature trees themselves that have become popular around the world.
Like many things, this art migrated from China to Japan some time ago, but we tend to associate it with Japanese culture and even use the Japanese word in English.
Granted, in the present day, this hobby seems to be more popular in Japan but still has a great following in China and even a little in Korea as well.
Note: Many people confuse the title of the bonsai tree with “banzai” which is a form of “hooray” in Japanese. I have also seen it misspelled as “bansai.” The correct Romanization (Romaji) is “bonsai.”
Flowers / Blooming / Splendid / China
華 means blooming flowers or splendid China.
華 is really open to interpretation. 華 meant flowers or blooming in ancient China. It still has that meaning in Japanese, and Buddhist contexts.
In modern China, this means glorious, beautiful, splendid, magnificent, or the best part of something. It can also refer to the country of China or something Chinese (such as people - overseas Chinese are often called “hua ren”). 華 is also a surname in China.
In Japanese, this can be the female given name “Ririka.” It's also the short name for a certain kind of playing cards in Japan.
In Korean, This can be the surname “Hwa.” While it also means splendid, flowery, or the country of China in Korean.
Ice / Frost
冰 is the Japanese Kanji for “ice” or “frost.”
冰 is also the way to write “ice” in old Korean Hanja.
Note: This form is not commonly used anymore in Chinese - though still understood for the most part.
FYI: There was a time when Japan did not have a written language and simply absorbed Chinese characters into their language by meaning. When this occurred around the 5th century, the character shown here was a common but alternate way to write “ice” in Chinese, so it was the one that ended up being absorbed into the Japanese language. Not long after that, a similar thing happened in Korea - although Korea has replaced virtually all of the Chinese characters they once used with the new Hangul writing system.
Prosperity
繁栄 is the same “prosperity” as the Traditional Chinese version, except for a slight change in the way the second character is written (it's the Japanese Kanji deviation from the original/ancient Chinese form).
Chinese people will still be able to read this, though you should consider this to be the Japanese form (better if your audience is Japanese).

Sometimes, the Kanji form shown to the right is used in Japanese. It will depend on the calligrapher's mood as to which form you may receive. If you have a preference, please let us know at the time of your order.
Cuong Nhu
剛柔 is a term that means hardness and softness or hard and soft.
剛柔 is also the Chinese character origin of the martial arts style known as Cương Nhu.
Cương Nhu or Cuong Nhu was founded by Grandmaster Ngo Dong in 1965 in Hue, Vietnam, and brought to the U.S. in 1971.
剛 means hard, firm, strong, and just.
柔 means soft, flexible, supple, yielding, softness, and/or gentleness.
Until it was romanized in the mid-17th century by Portuguese missionaries with later influence by French missionaries, Vietnamese was exclusively written in Chinese characters. With some research, you can still figure out the original way to write most Vietnamese words and titles in Chinese characters. That is what I did here to figure out that Cuong Nhu would have been 剛柔 if established in ancient Vietnam.
Same characters are used in Japanese for various Goju schools of Okinawan martial arts, though not the same lineage as the Vietnamese style described above.
Better to be Happy than Rich
安貧樂道 means “It's better to be happy than rich” in Chinese.
Even if you are poor, you should still feel satisfied in your life...
...Satisfaction, happiness and the meaning of your life come from within yourself and not from money or riches of the world.
In Chinese, there are a lot of four-character proverbs which express some very old philosophies.
Though there are only four characters on this scroll, in Chinese, the meanings often surpass the dictionary definition of each character.
In this case, you should not set your expectations too high for the money or riches you wish to have. One who sets their expectations too high is almost always disappointed. Instead, you should cherish what you have, seek to improve yourself from within, and not measure your worth by the size of your bank account.
Goddess of Mercy and Compassion
觀音/観音 is the Buddhist deity known as the Goddess of Mercy or Bodhisattva of Compassion.
In Chinese, the proper name of this being is Guan Yin. There is some debate as to whether Guan Yin is female. The argument comes from some scripture that suggests Buddhist deities take on the male form. Others say that Guan Yin has no sex. And still, others are okay with the female representation of Guan Yin.
This bodhisattva is also known or Romanized in the following ways:
Mandarin Chinese: Guan Yin, Kuan Yin, Kwan Yin.
Japanese: Kannon, Kwannon.
Sanskrit: Bodhisattva Avalokitesvara.
Korean: Gwan-eum.
Vietnamese: Quan Âm.
Thai: Kuan Eim.
English: Bodhisattva of Mercy and Salvation, Goddess of Compassion, Buddha of Mercy, et al.
Note: The first character has a slight variation in Japanese. If your audience is specifically Japanese, you may want to select that version.
See Also: Buddhism | Goddess | Namo Amitabha | Bodhisattva
Law of the Fist Karate / Kempo Karate
The first two characters mean “fist law” which is Romanized from Japanese as “Kenpo” or “Kempo.”
The last two are a secondary way to express “karate.”
Notes:
The more common way to express “karate” is literally “empty hand” (meaning “without weapons in your hand”). This version would be translated literally as “Tang hand” (as in the Tang Dynasty) or “China hand” (sometimes “Tang” means “China” in Japanese). Even though the character for “Tang” is used instead of “empty,” it's still pronounced “kara-te” in Japanese.
拳法唐手 is not commonly used in China - so please consider it to be a Japanese-only title.
Many Japanese people will say the last two Kanji are the old and antiquated way of saying Karate. This fact does not stop this title from existing, as these four characters are often seen in Kenpo / Kempo Dojos around the western world.
Life Energy / Spiritual Energy
Chi Energy: Essence of Life / Energy Flow
This 氣 energy flow is a fundamental concept of traditional Asian culture.
氣 is romanized as “Qi” or “Chi” in Chinese, “Gi” in Korean, and “Ki” in Japanese.
Chi is believed to be part of everything that exists, as in “life force” or “spiritual energy.” It is most often translated as “energy flow” or literally as “air” or “breath.” Some people will simply translate this as “spirit,” but you must consider the kind of spirit we're talking about. I think this is weighted more toward energy than spirit.
The character itself is a representation of steam (or breath) rising from rice. To clarify, the character for rice looks like this: ![]()
Steam was apparently seen as visual evidence of the release of “life energy” when this concept was first developed. The Qi / Chi / Ki character is still used in compound words to mean steam or vapor.
The etymology of this character is a bit complicated. It's suggested that the first form of this character from bronze script (about 2500 years ago) looked like these samples: 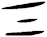
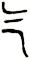
However, it was easy to confuse this with the character for the number three. So the rice radical was added by 221 B.C. (the exact time of this change is debated). This first version with the rice radical looks like this: 
The idea of Qi / Chi / Ki is really a philosophical concept. It's often used to refer to the “flow” of metaphysical energy that sustains living beings. Yet there is much debate that has continued for thousands of years as to whether Qi / Chi / Ki is pure energy or consists partially or fully of matter.
You can also see the character for Qi / Chi / Ki in common compound words such as Tai Chi / Tai Qi, Aikido, Reiki, and Qi Gong / Chi Kung.
In the modern Japanese Kanji, the rice radical has been changed into two strokes that form an X.
![]() The original and traditional Chinese form is still understood in Japanese, but we can also offer that modern Kanji form in our custom calligraphy. If you want this Japanese Kanji, please click on the character to the right instead of the “Select and Customize” button above.
The original and traditional Chinese form is still understood in Japanese, but we can also offer that modern Kanji form in our custom calligraphy. If you want this Japanese Kanji, please click on the character to the right instead of the “Select and Customize” button above.
More language notes: This is pronounced like “chee” in Mandarin Chinese, and like “key” in Japanese.
This is also the same way to write this in Korean Hanja where it is Romanized as “gi” and pronounced like “gee” but with a real G-sound, not a J-sound.
Though Vietnamese no longer use Chinese characters in their daily language, this character is still widely known in Vietnam.
See Also: Energy | Life Force | Vitality | Life | Birth | Soul
Honor
(Modern Japanese version)
名譽 is a version of honor that is about having or earning the respect of others and about your reputation.
It is the status of being worthy of honor (not to be confused with doing honorable things or specific actions - see our other “honor” listing for that).
![]() Both modern Japanese and modern mainland Chinese use the same simplified version of the second character of honor. You can make a special request for the traditional second character as shown to the right (just click on that character to the right of you want to order that version). Before WWII, both Japan and China used the traditional form but modern Japanese and Chinese use this simplified form. Koreans still use the traditional form when they are not writing in their modern Hangul glyphs.
Both modern Japanese and modern mainland Chinese use the same simplified version of the second character of honor. You can make a special request for the traditional second character as shown to the right (just click on that character to the right of you want to order that version). Before WWII, both Japan and China used the traditional form but modern Japanese and Chinese use this simplified form. Koreans still use the traditional form when they are not writing in their modern Hangul glyphs.
This is also a virtue of the Samurai Warrior
See our page with just Code of the Samurai / Bushido here
Devotion / Dedication / Attentive / Focused
專心 makes a word that means “paying attention with your heart.”
It's often translated as “dedication,” as in “be absorbed in” or “concentrate one's efforts.” It's also used to mean “with the single mind,” “whole-heartedly,” “paying attention,” “undivided attention,” “concentration (-ed),” “engrossed,” “devotionally (listening/watching),” and/or “attentive.”
The first character means “for a particular person, occasion, or purpose,” “focused on one single thing,” “concentrated,” and sometimes, “special.”
The second character means “heart” or “mind” by itself.
My favorite translation, which comes from the Oxford Advanced Chinese/English Dictionary, is, “wholehearted devotion.”
If it seems like the meaning of this word is quite open, you are correct. The context in which the word is used matters a lot. It can mean different things depending on how you use it. This makes it kind of nice as you can decide what this means to you (within some limits). This is always positive in meaning, so even if a Chinese person reads it differently than you, it will still have a good meaning.
![]() In Japanese, they tend to use a variation of the second character which has one less stroke. If you want your calligraphy written this Japanese form, please click on the Kanji shown to the right instead of the button above. Note: Japanese and Chinese people will recognize either form.
In Japanese, they tend to use a variation of the second character which has one less stroke. If you want your calligraphy written this Japanese form, please click on the Kanji shown to the right instead of the button above. Note: Japanese and Chinese people will recognize either form.
Sword
劍 is pronounced “jian” in Chinese. When you say it, imagine that you are making the sound of a sword as it clashes with a metal shield. This might get you closer to the correct pronunciation in Chinese.
I actually wonder if this word came from the metallic ringing sounds of a sword in battle - but such knowledge is lost in history.
The sword is a symbol of a warrior. The one thing that a soldier in ancient China lived and died by. A warrior with his skills and sword proves himself of great value. A warrior who losses his sword instantly becomes worthless.
劍 is an excellent scroll for someone in the military (especially officers of all services - as well as enlisted NCO Marines since they still carry swords even if mainly for ceremonial purposes). Or perhaps someone who practices variations of kung fu or tai chi that involve weapons.
Please note that while this character is understood with the sword meaning in Japanese, you might be looking for the word “katana” which also means sword in Japanese but means “knife” in Chinese.
There are other ways to write sword, and here are a few...
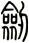
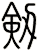
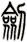
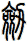
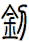


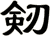

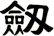
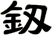



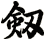
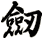
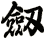
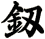






![]()
![]()
![]()
![]()

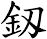
If you are particular about the version you receive, please let me know when you place your order (Note: Special styles are only available from one of our master calligraphers).
Master / Skilled Worker
Secondary version of Sifu
師傅 is “sifu” as in the “master” in the context of martial arts.
But two sifu titles are floating around. This one can simply mean “skilled worker.”
Historically, this term has been used for many things, such as “The tutor of a king or emperor.” But now it's more commonly used to mean master worker or qualified worker.
Currently, within the field of skilled labor, a master (Shifu) is higher than a journeyman and is considered to be one worthy of teaching others.
Note: In the 1970s and 1980s, this term was used as a common form of polite address between people. You might say, “master, do you know where Tian'anmen Square is?” to a person on the street at that time. This usage has almost passed; however, for some reason, people still often refer to taxi cab drivers as “master” in China (though I think/hope this is fading).
In Mandarin Chinese, this is pronounced like “Sure Foo,” and in Cantonese, like “See Foo.”
The second character is the difference between this sifu and the other. In this case, the second character by itself means tutor, instructor, or teacher.
Confucius
孔子 is how to write the name of the great sage, known in the West as Confucius.
His real name is Kongzi (The name Confucius is a westernized version of his name - his family name is Kong, and “zi” was added as a title of distinction).
He lived some 2500 years ago in Qufu, a town in modern-day Shandong Province of Northern China (about 6 hours south of Beijing by bus). He was a consort to Emperors, and after his death, the impact of his philosophies still served to advise emperors, officials, and common people for generations.
Also during these thousands of years, the Kong family remained powerful in China, and the Kong estate was much like the Vatican in Rome. The Kong estate existed as if on sovereign ground with its own small garrison of guards and the privileges of a kingdom within an empire.
This was true up until the time the Kong family had to flee to Taiwan in 1949 when the Red Army took victory over the Nationalists during the Revolution. The home of Confucius was later razed and all statues were defaced or stolen during the Cultural Revolution. Finally, after years of smearing his name and image, it is once again okay to celebrate the teachings of Confucius in mainland China.
Known as Khổng Tử in Vietnamese.
Banzai / Wansui
Old Japanese / Traditional Chinese & Korean
萬歲 is the traditional Chinese, Korean Hanja, and ancient Japanese way of writing banzai.
In modern times, the first character was simplified in Japan and China. So you might want to select the other entry for universal readability.
While it has become a popular, if not an odd, thing to scream as you jump out of an airplane (preferably with a parachute attached), banzai is actually a very old Asian way to say “hooray.” The Japanese word “banzai” comes from the Chinese word “wan sui,” which means “The age of 10,000 years.” It is actually a wish that the Emperor or the Empire live that long.
Imagine long ago when the Emperor made a rare public appearance. 萬歲 is what all people would yell to their leader in respect.
So if you like it as a hooray, or you want to wish someone that they live for 10,000 years, this is the calligraphy for you.
Other translations include Cheers! (not the drinking kind), hurrah!, long live [name]!, and congratulations!
To other things with banzai in their names, I am still waiting for the promised sequel to Buckaroo Banzai.
Notes: Sometimes people confuse banzai with bonsai. A bonsai is a miniature tree. They have nothing to do with each other.
Drain the pond to get all the fish
Kill the goose that lays the golden eggs
In 632 BC, Duke Wen of the Kingdom of Jin was about to lead an army against the forces of the Kingdom of Chu.
The Duke asked one of his advisers, Jiu Fan, how they could win the impending battle, as they were drastically outnumbered.
Jiu Fan said, “All is fair in war,” and suggested a plan of dishonorable tactics (cheating).
The Duke was unsure of this advice, so he asked another adviser, Yong Ji, who replied, “If you catch fish by draining the pond, you can certainly get all the fish. But there will be no fish the following year. You can cheat this one time in battle, but such tactics can only be used once, as the enemy will be wise in future encounters.”
The Duke heard the words of his wiser adviser but cheated to gain victory in the battle. However, he rewarded Yong Ji more than Jiu Fan at the victory celebration, stating that while Jiu Fan's advice gained one victory, the wise words of Yong Ji would last forever.
This Chinese idiom/proverb is still used, over 2600 years later to remind people not to burn bridges, cheat, or dishonor themselves in exchange for a short-term gain while sacrificing the future.
竭澤而漁 is very similar to the meaning of the English phrase, “Kill the goose that lays the golden eggs.”
In Wine there is Truth
酒后吐真言 / 酒後吐真言 is a nice Asian proverb if you know a vintner or wine seller - or wine lover - although the actual meaning might not be exactly what you think or hope.
The literal meaning is that someone drinking wine is more likely to let the truth slip out. It can also be translated as “People speak their true feelings after drinking alcohol.”
It's long believed in many parts of Asia that one can not consciously hold up a facade of lies when getting drunk, and therefore the truth will come out with a few drinks.
I've had the experience where a Korean man would not trust me until I got drunk with him (I was trying to gain access to the black market in North Korea which is tough to do as an untrusted outsider) - so I think this idea is still well-practiced in many Asian countries.
Please note that there are two common ways to write the second character of this phrase. The way it's written will be left up to the mood of the calligrapher, unless you let us know that you have a certain preference.
A sly rabbit has three openings to its den
-or- The crafty rabbit has three different entrances to its lair
狡兔三窟 speaks to the cunning character of a sly rabbit. Such a rabbit will not have just one hole but rather a few entrances and exits from his liar.
About 2,250 years ago, a rich man told his assistant to go and buy something wonderful that he did not yet possess. He was a man that already had everything, so the assistant went to a local village that owed a great deal of money to the rich man. The assistant told the village elders that all debts were forgiven. All the villagers rejoiced and praised the rich man's name. The assistant returned to the rich man and told him he had purchased “benevolence” for him. The rich man was mildly amused but perhaps slightly confused by the action.
Sometime later, the rich man fell from the favor of the Emperor and was wiped out without a penny to his name. One day he was walking aimlessly and stumbled into the village where the debts had been forgiven. The villagers recognized the man and welcomed him with open arms, clothed, fed him, and gave him a place to live.
Without trying, the man had become like the sly and cunning rabbit. When his exit was blocked, he had another hole to emerge from - and was reborn. This story and idiom come from a book titled “The Amendment” - it's unclear whether this man actually existed or not. But the book did propel this idiom into common use in China.
Still today, this idiom about the rabbit is used in China when suggesting “backup plans,” alternate methods, and anyone with a good escape plan.
Gung Ho
Working Together
工合 is one of those Asian words that is used more in English than in the original Chinese.
Gung Ho was originally used to speak of Carlson's Raiders, a group of “Gung Ho” U.S. Marines who went on an island-hopping campaign of death during WWII.
A movie called Gung Ho came out in the mid-1940s and was later re-released in the 1950s depicting the 2nd Marine Raider Battalion, and brought this word to the mainstream.
It is still sometimes used today within the U.S. Marine Corps brotherhood to refer to a unit or group that works well together or is otherwise efficient and motivated (has good morals).
In 1986, there was a movie called Gung Ho about a Japanese company taking over an American automotive factory. They completely ignored the fact that this was a Chinese title.
It should be noted that this title actually means a condition, state, manner, or the health of something in Japanese.
Language and pronunciation notes:
Like many Asian words absorbed into common use in English, this one is drastically mispronounced. The official Romanization is “gong he” but that doesn't tell you enough. The vowel sound on the first character is like the English word “own,” now just add the g-sounds to the beginning and end. The second character is misleading, as you might think it is like the English word “he.” In reality, the vowel sound is more like the “u” in “up.”
It should also be noted that the current generation in China no longer uses or recognizes this as a common word or slogan.
Note: This can be pronounced and is a word in Japanese, though seldom used. Japanese will use a variation of "具合" instead. But still, not common.
Qi Gong / Chi Kung
氣功 or Qigong is the title of a technique that is somewhere between medical practice, meditation, and in some cases, religion.
The definition is blurred depending on which school of Qigong you are following. In some cases, it is even incorporated with martial arts.
Some people (even Chinese people) mix this title with Tai Chi (Tai Qi) exercises.
Lately, in China, people will claim to practice Tai Chi rather than Qigong because the Qigong title was recently used as a cover for an illegal pseudo-religious movement in China with the initials F.G. or F.D. (I can not write those names here for fear of our website being banned in China).
You can learn those names and more here: Further info about Qigong
If you are wondering why I wrote “Qi Gong” and “Chi Kung” as the title of this calligraphy entry, I should teach you a little about the various ways in which Chinese can be Romanized. One form writes this as “Chi Kung” or “Chikung” (Taiwan). In the mainland and elsewhere, it is Romanized as “Qi Gong” or “Qigong.” The pronunciation is the same in Taiwan, mainland, and Singapore Mandarin. Neither Romanization is exactly like English. If you want to know how to say this with English rules, it would be something like “Chee Gong” (but the “gong” has a vowel sound like the “O” in “go”).
Romanization is a really confusing topic and has caused many Chinese words to be mispronounced in the west. One example is “Kung Pao Chicken,” which should actually be more like “Gong Bao” with the “O” sounding like “oh” for both characters. Neither the Romanization system in Taiwan nor the Mainland is perfect, in my opinion, and leads to many misunderstandings.
In modern Japan, you may see this written as 気功, but the original 氣功 is still recognized. If you need the Japanese version, please contact me.
Reiki
靈氣 is the title of a healing practice now found globally but with origins in Japan.
Special note: Outside of the context of the healing practice of Reiki, this means “aura” or “spiritual essence that surrounds all living things.” A Japanese person unfamiliar with the practice will take the “aura” meaning.
Reiki is a technique for stress reduction and relaxation that also heals. It can be compared to massage but is based on the idea that an unseen “life force energy” flows through us and is what causes us to be alive. If your life force energy is low, you'll be more likely to get sick or feel stressed. If your life force energy is abundant and flowing well, you become more capable of being happy and healthy.
There is a lot of information available if you want to Google this term - my job is to offer the calligraphy while you can decide if it is right for you.
Note: We are showing the ancient (traditional) form of the Reiki Kanji. I have seen Reiki written with the slightly simplified version and this more classic form. If you want the form of Reiki with the two strokes in the shape of an X on the second character and the modern first character, simply click on the Kanji characters to the right.
Note: 靈氣 is also a Chinese word, but in Chinese, these characters create a word that refers to a smart person or someone with high aspirations. It is not read as a healing method in Chinese.
In Korean Hanja, this can be read as a “mysterious atmosphere” by a Korean who is not familiar with the practice of Reiki (still has a cool meaning in Korean).
Zen / Chan / Meditation
...as in Zen Buddhism
First, let's correct something: The Japanese romanization for this character, “Zen” has penetrated the English language. In English, it's almost always incorrectly used for phrases like “That's so zen.” Nobody says, “That's so meditation” - right? As the title of a sect, this would be like saying, “That's so Baptist!"
禪 by itself just means “meditation.” In that context, it should not be confined to use by any one religion or sect.
Regardless of the dictionary definition, more often than not, this character is associated with Buddhism. And here is one of the main reasons:
Zen is used as the title of a branch of Mahayana Buddhism, which strongly emphasizes meditation practice.
However, it should be noted that Buddhism came from India, and “Chan Buddhism” evolved and developed in medieval China. The Chinese character “Chan” was eventually pronounced as “Zen” in Japanese. Chan Buddhists in China have much in common with Zen Buddhists in Japan.
More about the history of Zen Buddhism here.
Please also note that the Japanese Kanji character for Zen has evolved a little in Japan, and the two boxes (kou) that you see at the top of the right side of the character have been replaced by three dots with tails.
 The original character would still be generally understood and recognized in Japanese (it's considered an ancient version in Japan) but if you want the specifically modern Japanese version, please click on the zen Kanji to the right. Technically, there is no difference between the Tensho and Reisho versions of Zen since they are ancient character styles that existed long before Japan had a written language.
The original character would still be generally understood and recognized in Japanese (it's considered an ancient version in Japan) but if you want the specifically modern Japanese version, please click on the zen Kanji to the right. Technically, there is no difference between the Tensho and Reisho versions of Zen since they are ancient character styles that existed long before Japan had a written language.![]() There is also an alternate/shorthand/simplified Chinese version, which has two dots or tails above the right-side radical. This version is also popular for calligraphy in China. If you want this version, just click the character to the right.
There is also an alternate/shorthand/simplified Chinese version, which has two dots or tails above the right-side radical. This version is also popular for calligraphy in China. If you want this version, just click the character to the right.
Further notes: Zen is just one of seven sects of Buddhism practiced in Japan. The others are 律 Ritsu (or Risshū), 法相 Hossō, 論 Sanron 華嚴 Kegon, 天台 Tendai, and 眞言 Shingon.
Broken Mirror Rejoined
Used in modern times for divorced couples that come back together
破鏡重圓 is about a husband and wife who were separated and reunited.
About 1500 years ago in China, there lived a beautiful princess named Le Chang. She and her husband Xu De Yan loved each other very much. But when the army of the Sui Dynasty was about to attack their kingdom, disposed of all of their worldly possessions and prepared to flee into exile.
They knew that in the chaos, they might lose track of each other, so the one possession they kept was a bronze mirror which is a symbol of unity for a husband and wife. They broke the mirror into two pieces, and each of them kept half of the mirror. They decided that if separated, they would try to meet at the fair during the 15th day of the first lunar month (which is the lantern festival). Unfortunately, the occupation was brutal, and the princess was forced to become the mistress of the new commissioner of the territory, Yang Su.
At the Lantern Festival the next year, the husband came to the fair to search for his wife. He carried with him his half of the mirror. As he walked through the fair, he saw the other half of the mirror for sale at a junk market by a servant of the commissioner. The husband recognized his wife's half of the mirror immediately, and tears rolled down his face as he was told by the servant about the bitter and loveless life that the princess had endured.
As his tears dripped onto the mirror, the husband scratched a poem into his wife's half of the mirror:
You left me with the severed mirror,
The mirror has returned, but absent are you,
As I gaze in the mirror, I seek your face,
I see the moon, but as for you, I see not a trace.
The servant brought the inscribed half of the mirror back to the princess. For many days, the princess could not stop crying when she found that her husband was alive and still loved her.
Commissioner Yang Su, becoming aware of this saga, realized that he could never obtain the princess's love. He sent for the husband and allowed them to reunite.
This proverb, 破鏡重圓, is now used to describe a couple who has been torn apart for some reason (usually divorce) but have come back together (or remarried).
It seems to be more common these days in America for divorced couples to reconcile and get married to each other again. This will be a great gift if you know someone who is about to remarry their ex.
This in-stock artwork might be what you are looking for, and ships right away...
Gallery Price: $178.00
Your Price: $98.88
Dancing Minority Girl of Southern China Wall Scroll
Discounted Blemished
Gallery Price: $90.00
Your Price: $35.00
Gallery Price: $61.00
Your Price: $33.88
Gallery Price: $61.00
Your Price: $33.88
Gallery Price: $61.00
Your Price: $33.88
Gallery Price: $61.00
Your Price: $33.88
The following table may be helpful for those studying Chinese or Japanese...
| Title | Characters | Romaji (Romanized Japanese) | Various forms of Romanized Chinese | |
| Do not fear being slow, fear standing still | 不怕慢就怕站 | bú pà màn jiù pà zhàn bu2 pa4 man4 jiu4 pa4 zhan4 bu pa man jiu pa zhan bupamanjiupazhan | pu p`a man chiu p`a chan pupamanchiupachan pu pa man chiu pa chan |
|
| Calm Tranquility | 安 | an | ān / an1 / an | |
| Silent Solitary | 寂 | jaku | jì / ji4 / ji | chi |
| Faith is the bird that feels the light when the dawn is still dark | 信唸是在黎明前的黑闇中能感到光明的鳥 信念是在黎明前的黑暗中能感到光明的鸟 | xìn niǎn shì zài lí míng qián de hēi àn zhōng néng gǎn dào guāng míng de niǎo xin4 nian3 shi4 zai4 li2 ming2 qian2 de hei1 an4 zhong1 neng2 gan3 dao4 guang1 ming2 de niao3 xin nian shi zai li ming qian de hei an zhong neng gan dao guang ming de niao | hsin nien shih tsai li ming ch`ien te hei an chung neng kan tao kuang ming te niao hsin nien shih tsai li ming chien te hei an chung neng kan tao kuang ming te niao |
|
| Serenity Tranquility | 平靜 平静 | heisei | píng jìng ping2 jing4 ping jing pingjing | p`ing ching pingching ping ching |
| Inner Peace Silence Serenity | 靜 静 | shizu / sei | jìng / jing4 / jing | ching |
| Indomitable Spirit | 百折不屈 | bǎi shé bù qū bai3 she2 bu4 qu1 bai she bu qu baishebuqu | pai she pu ch`ü paishepuchü pai she pu chü |
|
| Sasuga Nagare | 流石 | ryuuzeki / nagareishi / nagare / sasuga ryuzeki / nagareishi / nagare / sasuga | ||
| Guo | 虢 | guó / guo2 / guo | kuo | |
| Even The 100-Foot Bamboo Can Grow One More Foot | 百尺竿頭更進一步 百尺竿头更进一步 | bǎi chǐ gān tóu gèng jìng yī bù bai3 chi3 gan1 tou2 geng4 jing4 yi1 bu4 bai chi gan tou geng jing yi bu baichigantougengjingyibu | pai ch`ih kan t`ou keng ching i pu pai chih kan tou keng ching i pu |
|
| Dragon Warrior | 龍戰士 龙战士 | lóng zhàn shì long2 zhan4 shi4 long zhan shi longzhanshi | lung chan shih lungchanshih |
|
| Palestine | 巴勒斯坦 | bā lè sī tǎn ba1 le4 si1 tan3 ba le si tan balesitan | pa le ssu t`an palessutan pa le ssu tan |
|
| Stay Strong Indestructible Unbreakable | 金剛不壞 / 金剛不壊 金刚不坏 | kon gou fu e kongoufue kon go fu e | jīn gāng bù huài jin1 gang1 bu4 huai4 jin gang bu huai jingangbuhuai | chin kang pu huai chinkangpuhuai |
| Always Try to do Better | 更に上を目指す | sara ni ue o me za su saraniueomezasu | ||
| Warrior Saint Saint of War | 武聖 武圣 | wǔ shèng / wu3 sheng4 / wu sheng / wusheng | ||
| Peaceful Tranquil Calm Free From Worry | 安寧 安宁 | an nei / annei | ān níng / an1 ning2 / an ning / anning | |
| Distance Runner | 長跑者 长跑者 | cháng pǎo zhě chang2 pao3 zhe3 chang pao zhe changpaozhe | ch`ang p`ao che changpaoche chang pao che |
|
| Shang | 尚 | nao | shàng / shang4 / shang | |
| Naginata Halberd | 薙刀 | naginata | ||
| Drink Up! Cheers! | 干杯 | gān bēi / gan1 bei1 / gan bei / ganbei | kan pei / kanpei | |
| The Sea of Knowledge Has No Limits | 學海無涯 学海无涯 | xué hǎi wú yá xue2 hai3 wu2 ya2 xue hai wu ya xuehaiwuya | hsüeh hai wu ya hsüehhaiwuya |
|
| Serenity Tranquility | 靜穏 静穏 | seion | ||
| Jew Jewish | 猶太 犹太 | yóu tài / you2 tai4 / you tai / youtai | yu t`ai / yutai / yu tai | |
| Persistence | 固執 固执 | koshuu / koshu | gù zhí / gu4 zhi2 / gu zhi / guzhi | ku chih / kuchih |
| Selflessness | 無私 无私 | mushi | wú sī / wu2 si1 / wu si / wusi | wu ssu / wussu |
| Sacrifice | 犧牲 / 犠牲 牺牲 | gi sei / gisei | xī shēng / xi1 sheng1 / xi sheng / xisheng | hsi sheng / hsisheng |
| Sparrow | 麻雀 | maa jan / maajan / ma jan | má què / ma2 que4 / ma que / maque | ma ch`üeh / machüeh / ma chüeh |
| Sit Quietly in Meditation | 入靜 入静 | rù jìng / ru4 jing4 / ru jing / rujing | ju ching / juching | |
| Secret | 密 | mitsu | mì / mi4 / mi | |
| A Deliberate Inaction is Better than a Blind Action | 一動不如一靜 一动不如一静 | yí dòng bù rú yí jìng yi2 dong4 bu4 ru2 yi2 jing4 yi dong bu ru yi jing yidongburuyijing | i tung pu ju i ching itungpujuiching |
|
| Manga | 漫画 | manga | màn huà / man4 hua4 / man hua / manhua | |
| Great Expectations | 望 | bou / nozomi bo / nozomi | wàng / wang4 / wang | |
| Kindheartedness Benevolence Humanity | 仁德 | jintoku | rén dé / ren2 de2 / ren de / rende | jen te / jente |
| Learning is Eternal | 學無止境 学无止境 | xué wú zhǐ jìng xue2 wu2 zhi3 jing4 xue wu zhi jing xuewuzhijing | hsüeh wu chih ching hsüehwuchihching |
|
| Sakasa Reverse | 逆さ | sakasa | ||
| Great Lord Tycoon | 大君 | tai kun / taikun | ||
| Ritsu | 律 | ritsu | lǜ / lu:4 / lu: | lü |
| Ichi-Dan First Degree | 一段 | ichi dan / ichidan | yī duàn / yi1 duan4 / yi duan / yiduan | i tuan / ituan |
| Tranquility Yields Transcendence | 寧靜致遠 宁静致远 | níng jìng zhì yuǎn ning2 jing4 zhi4 yuan3 ning jing zhi yuan ningjingzhiyuan | ning ching chih yüan ningchingchihyüan |
|
| Goddess of Compassion | 観音 | kan non / kannon | guān yīn / guan1 yin1 / guan yin / guanyin | kuan yin / kuanyin |
| Kingdom of Heaven | 天國 天国 | tengoku | tiān guó / tian1 guo2 / tian guo / tianguo | t`ien kuo / tienkuo / tien kuo |
| Strong and Beautiful | 健美 | takemi | jiàn měi / jian4 mei3 / jian mei / jianmei | chien mei / chienmei |
| Body | 身 | mi | shēn / shen1 / shen | |
| Dragon Emperor Symbol | 竜 | ryuu / tatsu ryu / tatsu | lóng / long2 / long | lung |
| Xing Yi Quan | 形意拳 | ke i ken / keiken | xíng yì quán xing2 yi4 quan2 xing yi quan xingyiquan | hsing i ch`üan hsingichüan hsing i chüan |
| Brief and to the Point | 言簡意賅 言简意赅 | yán jiǎn yì gāi yan2 jian3 yi4 gai1 yan jian yi gai yanjianyigai | yen chien i kai yenchienikai |
|
| Guan Gong Warrior Saint | 關公 关公 | guān gōng guan1 gong1 guan gong guangong | kuan kung kuankung |
|
| A Journey of 1000 Miles Feels Like One | 千里も一里 | sen ri mo ichi ri senrimoichiri | ||
| Chinese or Korean Army General | 將軍 将军 | shougun / shogun | jiāng jūn jiang1 jun1 jiang jun jiangjun | chiang chün chiangchün |
| Even a fool may sometimes come up with a good idea | 千慮一得 千虑一得 | senryonoittoku | qiān lǜ yī dé qian1 lv4 yi1 de2 qian lv yi de qianlvyide | ch`ien lü i te chienlüite chien lü i te |
| Boxing | 拳闘 拳斗 | ken tou / kentou / ken to | ||
| Banzai | 万歲 / 萬歲 万岁 | banzai | wàn suì / wan4 sui4 / wan sui / wansui | |
| Pain | 痛 | tsuu / ita / tsu / ita | tòng / tong4 / tong | t`ung / tung |
| My True Love | 我心真愛 我心真爱 | wǒ xīn zhēn ài wo3 xin1 zhen1 ai4 wo xin zhen ai woxinzhenai | wo hsin chen ai wohsinchenai |
|
| Caring | 關心 关心 | guān xīn / guan1 xin1 / guan xin / guanxin | kuan hsin / kuanhsin | |
| Everything Happens for a Reason | 物事は全て理由があって起きる | monogoto ha subete riyuu ga at te okiru monogoto ha subete riyu ga at te okiru | ||
| Bonsai Penzai | 盆栽 | bon sai / bonsai | pén zāi / pen2 zai1 / pen zai / penzai | p`en tsai / pentsai / pen tsai |
| Flowers Blooming Splendid China | 華 华 | ririka | huá / hua2 / hua | |
| Ice Frost | 冰 氷 | koori / kori | bīng / bing1 / bing | ping |
| Prosperity | 繁栄 繁荣 | hanei | fán róng / fan2 rong2 / fan rong / fanrong | fan jung / fanjung |
| Cuong Nhu | 剛柔 | gou juu / goujuu / go ju | gāng róu / gang1 rou2 / gang rou / gangrou | kang jou / kangjou |
| Better to be Happy than Rich | 安貧樂道 安贫乐道 | ān pín lè dào an1 pin2 le4 dao4 an pin le dao anpinledao | an p`in le tao anpinletao an pin le tao |
|
| Goddess of Mercy and Compassion | 觀音 / 観音 观音 | kan non / kannon | guān yīn / guan1 yin1 / guan yin / guanyin | kuan yin / kuanyin |
| Law of the Fist Karate Kempo Karate | 拳法唐手 | ken pou kara te kenpoukarate ken po kara te | quán fǎ táng shǒu quan2 fa3 tang2 shou3 quan fa tang shou quanfatangshou | ch`üan fa t`ang shou chüanfatangshou chüan fa tang shou |
| Life Energy Spiritual Energy | 氣 气 / 気 | ki | qì / qi4 / qi | ch`i / chi |
| Honor | 名譽 名誉 | meiyo | míng yù / ming2 yu4 / ming yu / mingyu | ming yü / mingyü |
| Devotion Dedication Attentive Focused | 專心 / 専心 / 耑心 专心 | sen shin / senshin | zhuān xīn zhuan1 xin1 zhuan xin zhuanxin | chuan hsin chuanhsin |
| Sword | 劍 剑 | ken / tsurugi | jiàn / jian4 / jian | chien |
| Master Skilled Worker | 師傅 师傅 | shī fu / shi1 fu / shi fu / shifu | shih fu / shihfu | |
| Confucius | 孔子 | koushi / koshi | kǒng zǐ / kong3 zi3 / kong zi / kongzi | k`ung tzu / kungtzu / kung tzu |
| Banzai Wansui | 萬歲 万岁 | banzai / manzai | wàn suì / wan4 sui4 / wan sui / wansui | |
| Drain the pond to get all the fish | 竭澤而漁 竭泽而渔 | jié zé ér yú jie2 ze2 er2 yu2 jie ze er yu jiezeeryu | chieh tse erh yü chiehtseerhyü |
|
| In Wine there is Truth | 酒后吐真言 / 酒後吐真言 酒后吐真言 | jiǔ hòu tǔ zhēn yán jiu3 hou4 tu3 zhen1 yan2 jiu hou tu zhen yan jiuhoutuzhenyan | chiu hou t`u chen yen chiuhoutuchenyen chiu hou tu chen yen |
|
| A sly rabbit has three openings to its den | 狡兔三窟 | jiǎo tù sān kū jiao3 tu4 san1 ku1 jiao tu san ku jiaotusanku | chiao t`u san k`u chiaotusanku chiao tu san ku |
|
| Gung Ho | 工合 | guai | gōng hé / gong1 he2 / gong he / gonghe | kung ho / kungho |
| Qi Gong Chi Kung | 氣功 气功 | ki kou / kikou / ki ko | qì gōng / qi4 gong1 / qi gong / qigong | ch`i kung / chikung / chi kung |
| Reiki | 靈氣 灵气 霊気 | reiki | líng qì / ling2 qi4 / ling qi / lingqi | ling ch`i / lingchi / ling chi |
| Zen Chan Meditation | 禪 禅 | zen | chán / chan2 / chan | ch`an / chan |
| Broken Mirror Rejoined | 破鏡重圓 破镜重圆 | pò jìng chóng yuán po4 jing4 chong2 yuan2 po jing chong yuan pojingchongyuan | p`o ching ch`ung yüan pochingchungyüan po ching chung yüan |
|
| In some entries above you will see that characters have different versions above and below a line. In these cases, the characters above the line are Traditional Chinese, while the ones below are Simplified Chinese. | ||||
Successful Chinese Character and Japanese Kanji calligraphy searches within the last few hours...



















 A naginata is a special kind of halberd or long sword carried by some Samurai and other warriors. It is still used ceremonially in some schools of martial arts.
A naginata is a special kind of halberd or long sword carried by some Samurai and other warriors. It is still used ceremonially in some schools of martial arts.






































































