Many custom options...
And formats...

Alone in Chinese / Japanese...
Buy an Alone calligraphy wall scroll here!
Personalize your custom “Alone” project by clicking the button next to your favorite “Alone” title below...
3. Alone with only your shadow for company
4. I Miss You
6. Lonely
10. Independence
11. Phenomenon
12. Laugh / Smile
13. Happiness / Joy
15. Fight for a Goal
16. Knight
18. Hitori
19. Grandfather
22. Strong / Robust
25. Power / Strength
26. Sitting Quietly
27. Color
29. Be Like Water
30. Dharma / The Law
31. Stone / Rock
32. Ocean
35. Darkness
36. Inspire
39. Brown
40. Bat
42. Kill / Slaughter / Murder / Butcher
43. Opportunity
44. Forgiveness
45. Best
46. Speed
47. Good Health / Healthy / Vigor
48. North American Opossum / Possum
49. Only the sleepless know the length of night
50. Vampire
51. Listen
53. Wellness
54. Peace of Mind
55. Adventure
60. Religious Devotion / Faith in God / Religious Faith
61. Happy / Laughter / Cheerful Bliss
63. Woman
64. Gaman
66. The Saint
67. Cooperation / Collaboration
68. Spirit / Spiritual Essence
69. Wolf
70. Che Guevara
71. Dynasty
72. Diligence
74. Purified Spirit / Enlightened Attitude
75. Fate / Opportunity / Chance
76. Student
78. Empress
79. Lingering Mind
80. Daoism / Taoism
81. Immovable Mind
84. Daodejing / Tao Te Ching - Chapter 54
Alone / Solitary Existence
獨居 is a Chinese word that can be translated as to live alone, to live a solitary existence, solitude, solitary life, dwelling alone.
You might use a word like this regarding a hermit.
![]() In modern Japan, and Simplified Chinese, they use the version of the first character shown to the right. If you want this version please click on the character to the right instead of the button above.
In modern Japan, and Simplified Chinese, they use the version of the first character shown to the right. If you want this version please click on the character to the right instead of the button above.
Alone / A Lone Person
Alone / A Lone Person
獨自 is a Japanese word that means “alone” in the context of a person by himself/herself.
This can be translated as individual, solo, on one's own, or by oneself.
See Also: I Miss You
Alone with only your shadow for company
煢煢孑立形影相吊 is a Chinese proverb about the state of being as alone as you possibly can be.
It can be translated as “Alone with only your shadow for comfort/company.”
See Also: I Miss You
I Miss You
Desire / Longing / Craving
慾 means desire, longing, appetite, wish, covetousness, greed, passion, desire, avarice, and craving.
慾 is universal in Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and Korean Hanja.
The context in which this character is used determines whether the meaning is good or bad. As a single character on a wall scroll, you get to decide what the definition is to you (hopefully more toward desire than greed).
![]() Please note that Japanese use a simplified version of this character - it also happens to be the same simplification used in mainland China. Click on the character to the right if you want the Japanese/Simplified version of desire.
Please note that Japanese use a simplified version of this character - it also happens to be the same simplification used in mainland China. Click on the character to the right if you want the Japanese/Simplified version of desire.
Lonely
孤獨 means lonely, solitude, loneliness, and lonesome.
In some contexts, it can mean reclusive, isolated, single, or solo.
孤獨 is a Japanese word but not a good selection for a wall scroll.
In Chinese, this will relay a rather sad feeling to anyone who reads this calligraphy on your wall.
![]() The version shown to the left is the Traditional Chinese and ancient Japanese version. In modern Japan and China they often use a different more simplified version of the second character (as shown to the right). If you want this Japanese/Simplified version, please click on the character shown to the right instead of the button above.
The version shown to the left is the Traditional Chinese and ancient Japanese version. In modern Japan and China they often use a different more simplified version of the second character (as shown to the right). If you want this Japanese/Simplified version, please click on the character shown to the right instead of the button above.
Independent Spirit
獨立精神 means independent spirit in Chinese.
The first two characters mean independent, independence, or to stand alone.
The last two characters mean spirit, spiritual, vigor, vitality, drive, mind, consciousness, thought, essence, heart, or soul.
With this information, you can make your translation combination such as “independent heart,” “stand-alone spirit,” or more creatively, “the drive to stand alone” in English. There are a lot of ways to interpret 獨立精神.
Defense / Defend
防 is a single Chinese character and Korean Hanja that means to protect, defend, guard against, prevent, ward off, or counter.
防 means the same thing in Japanese, though seldom seen alone as a single Kanji. When written alone, it could be the Japanese surname Fusegi.
Heart of Judo
This 柔 Kanji literally means flexible, pliable, gentle, or yielding.
柔 is also the first Kanji of the Japanese martial arts titles of Judo and Jujutsu (Jujitsu). In those cases, it's pronounced “ju” in Japanese. However, alone, the classic pronunciation is “yawara.” Some translate this Kanji (in the context of martial arts) as “The Heart of Judo.”
Please note that this just means pliable, gentle, and yielding in Chinese and old Korean Hanja. They do know what Judo and Jujitsu are but if this character is seen alone in China or Korea, people generally will not think of the martial arts context.
Independence
Besides meaning “to be independent,” this can also mean “to stand alone,” self-reliance or self-support.
![]() Modern Japanese use a simplified version of the first character of independence.
it’s
the same simplified version currently used in mainland China, so understood by most Chinese and all Japanese people. Click on the character to the right if you want the simplified/Japanese version.
Modern Japanese use a simplified version of the first character of independence.
it’s
the same simplified version currently used in mainland China, so understood by most Chinese and all Japanese people. Click on the character to the right if you want the simplified/Japanese version.
Phenomenon
I must first say that 現象 is an odd thing to put on a wall scroll in Asian cultures. It won't make a lot of sense alone unless you have a special or personal meaning that you attach to it for yourself.
These two characters mean phenomenon in Chinese, Japanese, and Korean Hanja. They can also be translated as “a happening,” depending on context.
The sum of these characters is a little different than their individual meanings. But I will break it down anyway...
The first character means present, existing, actual, apparent, now, or current.
The second character alone means pattern after, imitate, image, shape, sign (of the times), form, appearance, to be like, to resemble, to take after, to seem, or elephant.
Laugh / Smile
笑 simply means to laugh or smile.
Notes: In some contexts, it can mean “ridicule” in Korean Hanja. 笑 is not often seen alone in Japanese, though it is understood.
Happiness / Joy
禧 is the type of happiness known in the west as “joy.”
The radical on the right side of this character is often seen alone (with the same meaning - and we do recommend that version because it's more universal).
Lonely Soul / Lost Soul
孤魂 is a Chinese title that means “lonely soul.”
In the context of being a soul without a mate or all alone, this can be translated as a “lost soul.”
Fight for a Goal
爭 is the way to express the idea of fighting for a goal.
This can also mean struggling or arguing. 爭 is okay for a Chinese audience, and while it is a word in Korean, this character is seldom seen alone in Korean grammar.
Knight
Sangha / Order of Monks
僧 is the single-character or short form of Sangha, the Buddhist idea of community or order (of monks, nuns, or followers of the Buddha).
Alone, this character can simply mean “monk” (Just means monk in Japanese).
![]()
![]() Note that when writing this as Kanji, Japanese will tend to write this in the form shown to the right. If you select our Japanese master calligrapher, please expect this special Kanji form.
Note that when writing this as Kanji, Japanese will tend to write this in the form shown to the right. If you select our Japanese master calligrapher, please expect this special Kanji form.
Hitori
This is the Japanese given name 独 which romanizes as Hitori or Doku.
Originally this was written as 獨 but was simplified/modernized in Japan at some point.
独 can also be an abbreviation for Germany.
The actual meaning is alone, independent, single, sole, only, or solitary.
This is also a Simplified Chinese character, but most Chinese calligraphers would prefer to write the Traditional Chinese of 獨 instead of 独.
Grandfather
祖父 is a title for grandfather in Japanese.
In Chinese, this is specifically paternal grandfather.
This title alone is not normal for a calligraphy wall scroll.
Bravery / Courage
Courageous Energy
勇氣 is one of several ways to express bravery and courage in Chinese, Japanese, and Korean.
This version is the most spiritual. This is the essence of bravery from deep within your being. This is the mental state of being brave versus actual brave behavior. You'd more likely use this to say, “He is very courageous,” rather than “He fought courageously in the battle.”
The first character also means bravery or courage when it's seen alone. With the second character added, an element of energy or spirit is added. The second character is the same “chi” or “qi” energy that Kung Fu masters focus on when they strike. For this reason, you could say this means “spirit of courage” or “brave spirit.”
This is certainly a stronger word than just the first character alone.
Beyond bravery or courage, dictionaries also translate this word as valor/valour, nerve, audacity, daring, pluck, plucky, gallantry, guts, gutsy, and boldness.
This is also one of the 8 key concepts of tang soo do.
![]() While the version shown to the left is commonly used in Chinese and Korean Hanja (and ancient Japanese Kanji), please note that the second character is written with slightly fewer strokes in modern Japanese. If you want the modern Japanese version, please click on the character to the right. Both styles would be understood by native Chinese, Japanese, and many (but not all) Korean people. You should make your selection based on the intended audience for your calligraphy artwork. Or pick the single-character form of bravery/courage which is universal.
While the version shown to the left is commonly used in Chinese and Korean Hanja (and ancient Japanese Kanji), please note that the second character is written with slightly fewer strokes in modern Japanese. If you want the modern Japanese version, please click on the character to the right. Both styles would be understood by native Chinese, Japanese, and many (but not all) Korean people. You should make your selection based on the intended audience for your calligraphy artwork. Or pick the single-character form of bravery/courage which is universal.
Perception of Knowledge
知識 has the very strong meaning of “knowledge” and, in some contexts, “learning.”
The first character represents “to know” or “to realize.”
The second character alone refers to the ability to “recognize” or “realize” and can also be used to mean “knowing.”
See Also: Wisdom | Learn From Wisdom
Strong / Robust
This “strong” character means “to strengthen” or robust. This brings images of a muscle-bound hulk of a weight lifter or bodybuilder to an Asian person who sees this character.
Note that in Korean and Japanese, this character is normally part of compound words, and is not seen alone too often.
![]() Note that the this character was simplified in Japan after WWII (also simplified in mainland China but not for calligraphy). If you want the modern Japanese/simplified version, please click on the Kanji shown to the right.
Note that the this character was simplified in Japan after WWII (also simplified in mainland China but not for calligraphy). If you want the modern Japanese/simplified version, please click on the Kanji shown to the right.
Hurricane / Typhoon
颱風/台風 is the most common way to write hurricane or typhoon in Chinese, old Korean Hanja, and Japanese Kanji. Sometimes used to refer to a big tornado as well.
The first character alone also means typhoon, but the second character means wind and acts to emphasize the meaning.

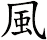 Note: Sometimes the first character is written in the form shown to the right.
Note: Sometimes the first character is written in the form shown to the right.
Hurricane / Typhoon
Military Engineering
Power / Strength
力 is the simplest form of “power” or “strength.”
In Japanese, it is pronounced “chikara” when used alone, and “ryoku” when used in a sentence (there are also a few other possible pronunciations of this Kanji in Japanese).
In some contexts, this can mean ability, force, physical strength, capability, and influence.
Sitting Quietly
Alone, this word means quite sitting, to sit quietly, or to meditate.
If you add and change the context a bit, this could mean to stage a sit-in (perhaps a non-violent protest by Buddhist monks or people). But again, as a single word as calligraphy art, it is the sitting quietly in meditation meaning that will be perceived.
Color
顏色 is kind of a weird selection for a wall scroll, but we added it to our database at the request of a customer.
顏色 means “color” in Chinese. However, in Japanese, it would mean complexion, countenance, or expression. The last character is used alone in Japanese (and sometimes in Chinese with/as an adjective/modifier) to mean “color.”
Tenacious / Tenacity
頑強 means “Tenacious,” “Hard to Defeat,” or “Dogged.”
Alone, the first character means mischievous, obstinate, or stubborn. But it loses some of the mischievous meaning when the second character is added.
The second character means strength, force, power, or better.
See Also: Determination | Dedication | Devotion | Never Give Up
Be Like Water
像水一樣 is a short quote from a much longer statement by Bruce Lee.
He summarized how people should be flexible to all circumstances, attacks, or situations. In the end, he exclaims, “Be like water, my friend.” 像水一樣 is the “Be like water” part alone since that seems to be what most people want.
Dharma / The Law
法 is the simple way to write “law” or in a Buddhist context “Dharma.”
This can also mean method, way, or Buddhist teaching. It's also an abbreviation for the country of France.
The Buddhist context exists in Chinese and Korean Hanja but I have not yet confirmed that this means more than “law” when used alone in Japanese.
Stone / Rock
石 is the character that means rock or stone in both Chinese and Japanese.
Alone, this will be read as “stone” in Japanese but in some context, it is a unit of measure for the volume of about five bushels.
This can also refer to a gem or jewel.
This can also be the Japanese surnames that romanize as Ishi, Tsuruishi, Soku, Seki, Shi, Kazu, Iso, Ishizaki, Ishisaki, or Koku.
Ocean
This is the Chinese and old Korean Hanja word for ocean. This can be pronounced in Japanese, and has the same meaning but is rarely seen alone in Japanese.
Besides ocean or sea, this character can also mean foreign, wide, or vast.
It's more common for Chinese people to use a different word “hai” for ocean or sea.
Great Expectations
望 holds the ideas of ambition, hope, desire, aspiring to, expectations, looking towards, to gaze (into the distance), and in some contexts, full moon rising.
望 is one of those single characters that is vague but in that vagueness, it also means many things.
望 is a whole word in Chinese and old Korean but is seldom seen alone in Japanese. Still, it holds the meanings noted above in all three languages.
Loyalty to Duty or Master
忠 is the simplest way to write the word loyalty in Chinese and Japanese.
A single character like this leaves the meaning open. But alone, a Chinese or Japanese person would think of loyalty to duty or loyalty to one's master (in ancient times). I suppose that it could be loyalty to your boss or company in this day in age.
忠 can also mean fidelity or faithfulness.
This can also be romanized as “chung.”
Darkness
黑闇 is the two-character Chinese word for darkness.
The first character alone means black or dark.
The second character has several possible meanings, depending on context; They include: to shut the door, unilluminated, dark, gloomy, hidden, or secret.
Together, these two characters will, in most cases, be translated as dark or darkness.
Inspire
Beyond inspire or inspiration, 啟示 is a Chinese word that can mean enlightenment or revelation.
This is used as the Biblical revelation in the Chinese Bible, so it can also mean apocalypse depending on context.
Separately, the first character can mean: to open; to start; to initiate; to enlighten; to awaken; to state; to inform.
The second character alone can mean: to show; to reveal; to indicate; to proclaim.
Honesty / Fidelity
信 is another character that expresses the idea of honesty.
It can also mean truth, faith, belief in, fidelity, sincerity, trust, and/or confidence.
Some have included this in the list for the Bushido, although “makoto” is probably more common/popular.
Note: In some contexts, this character can mean a letter (mail), news, or envoy. However, alone, it will generally be read with the honesty-meaning.
See our page with just Code of the Samurai / Bushido here
See Also: Loyalty Trustworthiness Trustworthy
Calm / Tranquility
安 is used in a lot of compound words in the CJK world.
Alone, this character has a broad span of possible meanings. These meanings include relaxed, quiet, rested, contented, calm, still, to pacify, peaceful, at peace, soothing, or soothed.
安 and even the pronunciation was borrowed from Chinese and absorbed into both Japanese Kanji and Korean Hanja. In all these languages, this character is pronounced like “an.”
Brown
Single character for brown color
褐 is the most simple way to express brown in Chinese.
It also means brown in Japanese but this character is not often written alone in Japanese (they would tend to write 褐色 (brown color) to refer to brown or the color of tanned skin.
In some contexts, this can refer to gray or a dark color, or coarse hemp cloth.
In the Buddhist context, it can refer to a coarse serge (cheaply sewn clothing) hence poverty.
Note: In Taiwanese Mandarin, this is spoken with the 2nd or rising tone instead of the 4th or falling tone used in the mainland.
蝠 is the simplest way to write bat in Chinese and old Korean Hanja.
This also means bat in Japanese but is almost never written alone like this (it's often part of other titles for vampire bats or fruit bats).
In Chinese culture, the bat is a good luck charm, as the pronunciation is very similar to the word for “good luck” or “good fortune.” The character for bat (蝠) even looks like the good luck (福) character.
Justice / Righteousness
正義 means justice or righteousness in Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and old Korean Hanja.
Practicing justice and righteousness is being fair.
It solves problems, so everyone wins. You don't prejudge. You see people as individuals. You don't accept it when someone acts like a bully, cheats, or lies. Being a champion for justice takes courage. Sometimes when you stand for justice, you stand alone.
Note: This is also considered to be one of the Seven Heavenly Virtues.
Kill / Slaughter / Murder / Butcher
殺 is how to write “to kill” or “killing.”
殺 is an absolutely shocking word to have on a wall scroll. It will bewilder, scare, and perhaps offend any Chinese, Korean, or Japanese person who sees it. I do not in any way recommend this for a piece of calligraphy artwork. This entry is only here because our calligraphy search engine received so many requests for “kill.”
Note: In Korean Hanja, this character is not often used alone - see the other two-character entry for “kill.”
Opportunity
機 is an odd one - I've seen this on coffee cups and posters with the meaning of “opportunity.”
機 is a correct definition but this character also means “machine.” In fact, if you put the character for “flying” in front of this character, you have the Chinese word for “airplane” (literally: flying machine). Alone, on a wall scroll, it will be generally understood as “opportunity” but I want you to know this extra information before you make your selection. Note that in Japanese and Korean, this has a similar meaning but can also mean machine or loom.
See Also: Success
Forgiveness (from the top down)
容赦 is the kind of forgiveness that a king might give to his subjects for crimes or wrong-doings.
容赦 is a rather high-level forgiveness. Meaning that it goes from a higher level to a lower (not the reverse).
Alone, the first character can mean “to bear,” “to allow,” and/or “to tolerate,” and the second can mean “to forgive,” “to pardon,” and/or “to excuse.”
When you put both characters together, you get forgiveness, pardon, mercy, leniency, or going easy (on someone).
See Also: Benevolence
Best
至 is a little strange as calligraphy, but 至 would be the character that means “best” or “extreme” in Chinese and Korean.
The problem is, this is seldom used alone. It's mostly used in combination with other characters to make words like “best friend,” “best food,” and “best love.”
I do not recommend this character for a wall scroll. It's better if you find a more specific term that fits your circumstances.
Note: This can be pronounced in Japanese and has a similar meaning but it is rarely if ever used in modern Japanese.
Speed
高速 means “high speed” or “in high gear” in Chinese and Japanese Kanji.
In old Korean Hanja, it also means “high speed” but can also be a nickname for “rapid transit.”
高速 is the best selection if you want to say “speed” in regard to your race car, race boat, or lifestyle. You need this word, which literally means “high speed,” as the Asian word for “speed” alone does not suggest whether you mean fast or slow.
Good Health / Healthy / Vigor
Also suggests being at peace
康 is a single character that means good health or vigor in Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and old Korean Hanja.
康 can also mean peaceful, at ease, or abundant in some contexts.
Please note that this is rarely seen alone in Japanese Kanji. In Japanese, it is used both for health-related compound words and to denote the kouhou through koushou eras of Japan.
In Korean, this can also be the family name “Kang” (caution: not the only family name romanized as Kang in Korean).
North American Opossum / Possum
北美負鼠 is the full title for North American Opossum (aphesis spelling: Possum). The first two characters mean “North American” as an adjective. The third character means “carries” and refers to the marsupial pouch. The last character means “rat.” You could say the literal translation is “marsupial rat.”
Chinese opossums vary from the North American variety. If you were to use the last two characters alone, it may suggest the species native to China.
See Also: Year of the Rat
Only the sleepless know the length of night
不眠之夜长久交知人心 literally translates as: [Only one who does] not sleep, learns how long the night is; [Only by] long acquaintance [does one] learn a person ['s true] character.
Basically, this proverb suggests that we really need to experience something intimately and for a long time to really know everything about it.
This can also be translated as “Spending years with someone is the only way to know them.”
Note: Sometimes this proverb is split into just the first or second idea alone (first 5 or last 5 characters only).
Vampire
吸血鬼 is how to say “vampire” in Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and old Korean Hanja.
Quite literally, this means “Suck Blood Ghost” or, more naturally, in English, “Ghost Who Sucks Blood.” This title is also used for leeches and blood-sucking vermin.
Just like the word “vampire” in English, this title is used in Asian languages colloquially to refer to “cruel exploiters,” and especially in China, it can be used to refer to “capitalists exploiting the workers.”
Alone on a wall scroll, this will be understood with just the “vampire” or “bloodsucker” meaning.
Listen
聽 means to listen, hear, and obey (depending on context).
聽 is a stand-alone word in Chinese but is usually seen in compound words in Korean. Therefore, this title is best for a Chinese audience.
![]() The ancient form of this character is shown in the upper left. However, there is a modern Japanese Kanji version shown to the right. If you want this modern Japanese version, please let us know when you place your order.
The ancient form of this character is shown in the upper left. However, there is a modern Japanese Kanji version shown to the right. If you want this modern Japanese version, please let us know when you place your order.
Mantis / Praying Mantis
螳螂 is mantis or “praying mantis,” as it's often titled in English.
Technically speaking, this especially applies to the narrow-winged mantis (Tenodera angustipennis)
It is best to use this very common two-character Asian title for the mantis, as the second character alone can mean mantis or dragonfly (totally ambiguous).
This title is antiquated in Japanese, as they tend to write カマキリ (kama kiri) in Katakana to mean praying mantis.
![]() Note: There is an alternate form of this title which uses the character shown to the right instead of the first character shown above. This is uncommon in both Japan and China (if you really want it anyway, please let us know).
Note: There is an alternate form of this title which uses the character shown to the right instead of the first character shown above. This is uncommon in both Japan and China (if you really want it anyway, please let us know).
Wellness
身體健康 is how to express “wellness” in Chinese. The meaning is not much different than the idea of “good health.” The first two characters alone are often translated as “health.” Some will also translate this title as “physical health.”
If you want to fill your room with a feeling of wellness, this is the wall scroll for you.
This is also the ancient way to express wellness in Japanese Kanji and old Korean Hanja. The modern Japanese form is 身体健康 (the only difference is the second Kanji). Let me know if you need your calligraphy written in modern Japanese.
Peace of Mind
和平 is the Chinese order for these two characters, which means peace but can also be translated as amicability, specifically, or mildness. 和平 is often translated as a simple way to say “peace of mind.” This combination is used in Korean Hanja to mean “peace and harmony.”
Alone, the first character means peace and harmony.
The second character means balance when read by itself.
Note: 和平 are often seen in the opposite order in Japanese with the same meaning (You'll sometimes find them in this order in Japan, so either way is OK).
Adventure
If you lead a life of adventure (like I do), a 探險 wall scroll is for you.
Alone, the first character can mean “to explore,” “to search out,” or “to scout.” The second character holds the meanings of “dangerous” and “rugged.” Together these two characters create the word that means “adventure” or “to explore.”
探険 is a modern Japanese Kanji version, but it more precisely means exploration or expedition rather than adventure. 探險 is the old/ancient Japanese version used before WWII. Let us know if you want the modern Japanese version instead.
See Also: Bon Voyage | Travel
Mercy / Compassion / Love
慈 is the simplest way to express the idea of compassion.
This can also mean love for your fellow humans, humanity, or living creatures. Sometimes this is extended to mean charity.
This term is often used in a Buddhist or Christian context. The concept was also spoken of by Laozi (Lao Tzu) in the Dao De Jing (Tao Te Ching).
慈 is considered the direct translation of the Sanskrit word मैत्री (maitrī) Pali word मेत्ता (mettā). In this context, it means benevolence, loving kindness, and goodwill.
This Chinese character is understood in Japanese but is usually used in compound words (not seen alone). Also used in old Korean Hanja, so it's very universal.
See Also: Mercy | Benevolence | Forgiveness | Kindness
Tooth for a tooth
以牙還牙 is a phrase that often goes with “An eye for an eye,” even in Chinese. Revenge seems to cross all languages, cultures, and even species (animals are known to take revenge too).
If a Chinese person uses just one part of the full proverb, it will be this “tooth for a tooth” one. Although, we are more likely to say “eye for an eye” alone in English.
Chinese people may also read this with the meaning of “Bite me, and I will bite you back.” However, it literally means “tooth for a tooth” or “you take my tooth, I take yours.”
Joushiki Wo Koeru
This Japanese phrase, “常識を超える” or “Jōshiki Wo Koeru” means “beyond common sense.”
常識 alone can be translated as “common sense,” “good sense,” “common knowledge”,“general knowledge,” “common practice,” “accepted practice,” or “social etiquette.”
The rest of the phrase indicates exceeding, overtaking, surpassing, transcending, or an idea of going beyond something.
More ways to translate this whole phrase:
Over what was known.
Surpassing common sense.
Beyond the ordinary.
Going beyond conventional knowledge.
Beyond conventional wisdom.
Note: Because this selection contains some special Japanese Hiragana characters, it should be written by a Japanese calligrapher.
Reiki - Master Symbol
大光明 is the master symbol “Daikomyo” or “Dai Ko Myo,” which is usually associated with the healing practice of Reiki.
This title can be translated as “Great Bright Light.” This symbol, as used in Reiki, alludes to “Enlightened Nature” or the radiance of a purified soul or deity.
Pronunciations in Chinese and Korean are included above but this title has no meaning except when used by a Reiki practitioner. In fact, this title is not that well known by those outside the Reiki community in Japan.
In Chinese, this would be interpreted as “Great Bright Future” (the second two characters alone create a word that means “bright future” in Chinese).
Religious Devotion / Faith in God / Religious Faith
信仰 means firm belief, faith, persuasion, conviction, and sometimes religion or creed in Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and old Korean Hanja.
This clearly fits the religious connotation of the English word “devotion.”
This is often used to refer to a person of faith or a religious person.
This can be directly translated as “firm belief,” “creed,” “conviction,” or simply as “religious,” depending on context.
Some will also use this to mean “trust in God” in Japanese (though the term for God is not actually in this title).
It should be noted that this word is a little strange alone on a wall scroll.
While this can be pronounced in Japanese, it’s not a great selection for a wall scroll if your audience is Japanese.
See Also: Faith | Trust | Devotion | Trust | Trust in God
Happy / Laughter / Cheerful Bliss
樂 is a single-character form of happiness or bliss that holds the ideas of laughing and having a good time.
This can also be translated as happy, glad, enjoyable, fun, and sometimes, music.
This a really good character if your audience is Chinese.
This is not a word seen alone very often in Korean.
![]() In Japanese, this character is written like the image shown to the right. If you order this from the Japanese master calligrapher, it will look like this instead of the character shown above.
In Japanese, this character is written like the image shown to the right. If you order this from the Japanese master calligrapher, it will look like this instead of the character shown above.
Note: In Japanese, this has a meaning of comfort, ease, and enjoyment.
See Also: Joyfulness
Lost / Dazed and Confused
迷 is one of those characters that can mean a lot of different things depending on context. When written alone, as a single character on a wall scroll, it opens up the possibilities and allows you to decide what it means to you.
The key definition is “to be lost.” This could be physically or mentally lost. It can be someone lost in their thoughts, lost in an ocean, or just confused about where they are. The reason for the confused state may be due to internal or external reasons.
Here are some entries from various Asian dictionaries...
Chinese: lost, confused, bewilder, crazy about, fan, enthusiast, mystery.
Japanese: lost, astray, perplexed, in doubt, err, illusion.
Korean: lost, bewildered, fascinated, deluded.
Woman
The ancient way to say Woman
巾幗 is the very old way to say woman in Chinese.
A common title in ancient China, this actually refers to the scarf or head wrapping worn by virtually all women at that time.
巾幗 is kind of a cool way to say Woman now. The actual gender character alone on a wall scroll would actually look like a fancy sign for the woman's restroom (WC).
![]() If you are curious, the character to the right means female or woman. Knowing 女 is useful information if you are a woman searching for a toilet in China or Japan.
If you are curious, the character to the right means female or woman. Knowing 女 is useful information if you are a woman searching for a toilet in China or Japan.
Gaman
Gaman is a Zen Buddhist term from Japan that means “enduring the seemingly unbearable with patience and dignity.”
This title can also be translated as patience, perseverance, tolerance, or self-denial.
我慢 is also a Chinese Buddhist term with a different pronunciation. It comes from Sanskrit abhimāna or ātma-mada. Chinese Buddhism defines this very differently as “Egoism exalting self and depreciating others,” “self-intoxication,” or “pride.” Alone, the first character means “Me, I, or Self,” and the second character in a Buddhist context comes from Sanskrit māna and means pride, arrogance, self-conceit, looking down on others, superciliousness, etc.
I’m currently working with Japanese and Chinese translators to try and reconcile the true meaning or any commonality of this word between languages. For now, please only consider this if your audience is Japanese.
Heart / Mind / Spirit
心 would often be translated as “heart.”
However, because it was believed in Chinese culture for thousands of years that your consciousness and thoughts came from the big red organ in the middle of your chest, it also means “mind” or “spirit” and sometimes even “soul.”
In Korean, beyond heart, mind, and spirit, this character can mean moral, nature, mind, affections, intentions, core, and center. In fact, it is used in Chinese to mean “center” as well but only with another character in front of it. For instance, “medical center” or even “shopping center.” Separately and alone, it will not be read with that “center” meaning unless thought of as “the center of your soul.”
The Saint
聖 is the simple, single-character religious form of “saint” in Chinese (also holds the same meaning in Japanese and Korean, though rarely used alone like this).
This can also mean holy, sage, master, or priest.
Note: 聖 is often used in compound words (words of more than one character) to create further meanings. In compounds, it can mean holy, sacred, or divine.
聖 is also used as the first word for Spanish and English place names such as “San Diego” and “St. Louis” in Chinese (not Japanese).
In the Buddhist context, this can represent ārya or sādhu. And mean a sage; wise and good; upright, or correct in all his character; sacred, holy, or saintly.
Cooperation / Collaboration
協作 is a Chinese, Japanese, and old Korean word that means cooperation or collaboration.
Cooperation is working together and sharing the load. When we cooperate, we join with others to do things that cannot be done alone. We are willing to follow the rules which keep everyone safe and happy. Together we can accomplish great things.
The first character means “united” or “to coordinate.” The second character means “to do,” “to make,” or “to compose.” Knowing this, you can understand why together, these characters create a word that can be defined as “cooperation” in Chinese, Japanese, and Korean.
It is implied that you are cooperating to create some project or product.
See Also: Partnership
Spirit / Spiritual Essence
神 is the simplest way to write spirit in Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and old Korean.
This single character alone will conjure up ideas of the spiritual world. 神 can also be translated as “vital awareness” as in the fact that one must know they exist to exist (I think, therefore, I am).
Other translations include:
God, deity, mysterious, divine essence, lively, spiritual being, divinity, supernatural, soul, mind, nerves, and energy. In some extended context, it can mean genius or unusual.
Japanese romanizations vary a lot when this character is combined into other words. However, shin is the original pronunciation taken from Chinese into Japanese. You'll also see it romanized as kami, gami, jin, and a few others, depending on context.
Wolf
狼 is the character used to represent the elusive animal known as the wolf in both Chinese and Japanese.
If you are a fan of the wolf or the wolf means something special to you, this could make a great addition to your wall.
Do keep in mind, that much like our perception of wolves in the history of western culture, eastern cultures do not have a very positive view of wolves (save the scientific community and animal lovers). The wolf is clearly an animal that is misunderstood or feared the world over.
狼 is seldom used alone in Korean Hanja but is used in a compound word that means utter failure (as in a wolf getting into your chicken pen - or an otherwise ferocious failure). Not a good choice if your audience is Korean.
Che Guevara
Latin American / Cuban Revolutionary
切格瓦拉 is the name “Che Guevara,” as written (transliterated) in Mandarin Chinese.
 Once revered by Chinese people as a Socialist rebel, he's now just a historical figure that school children briefly learn about in China.
Once revered by Chinese people as a Socialist rebel, he's now just a historical figure that school children briefly learn about in China.
切格瓦拉 is because China used to be a truly-Communist/Socialist nation, and thus, other Communists and Socialists were heroes.
In modern China, with its free-market economy, those former heroes fade a little.
We are not offering the “Che” character alone, as few would associate it with Che Guevara, so you need the full name to be clear (minus Ernesto, which is his real first name).
Dynasty
代 is the word used to designate dynasties in Asia.
代 alone can mean generation; age; period; historical era; eon; world; society; reign; era. 代 comes after the name of the dynasty, for example, the Tang Dynasty is the “Tang Dai” in Chinese.
Some have suggested that the word dynasty comes from the Chinese word “dai” (as “dai” sounds like the first syllable of a dynasty). However, the word dynasty is derived from the Greek word δυναστεία (dunasteia) meaning lordship and/or domination.
Sometimes this word is used in a different context where it can mean to represent or substitute. In this case, it can mean representative of; on behalf of; acting for, e.g. to offer incense in place of another.
In ancient Japan, this could also be a “shiro” (a unit of land area equal to one-fiftieth of a tan or about 20 square miles).
Diligence
勤 is a single character that means diligence or “sense of duty” in Chinese and Korean (also understood in Japanese but not commonly seen as a stand-alone Kanji).
As a single character on a wall scroll, this will only be seen with this meaning. However, it can also mean industrious, hardworking, frequent, regular, constant, energy, zeal, fortitude, or virility.
In Buddhism, this can represent vīrya (viriya), the idea of energy, diligence, enthusiasm, or effort. It can be defined as an attitude of gladly engaging in wholesome activities, and it functions to cause one to accomplish wholesome or virtuous actions. Some Buddhists may even define this as “manliness” (a definition from a hundred years ago, before equality).
If you or someone you know is a hard worker (or needs a reminder to be diligent), then this is the wall scroll to have in your/their office.
Koi Fish / Nishiki Goi
If you like or collect and maintain koi fish, 錦鯉 is the wall scroll for you.
Technically, this is a certain and revered species of “koi fish” in Japan, but it is the most normal selection for a wall scroll (more normal than the actual Kanji for “koi” or “fish” alone.
This literally means “brocade carp” or “embroidered carp.” This term is also used to mean the same thing in China (which is the origin of koi fish breeding and cultivation, several generations before they became popular in Japan).
For those of you that don't know, the Kanji for “koi” (which is pronounced “goi” in this entry) really means “carp.” If you want the word that means “koi fish,” it would just be the generic word for “carp fish.” That would include both colorful carp and the more mundane gray carp (the ones people eat if they don't mind lots of bones).
Purified Spirit / Enlightened Attitude
A Japanese martial arts title/concept
The first Kanji alone means to wash, bathe, primness, cleanse or purify.
The second Kanji means heart, mind, soul, or essence.
Together, these two Kanji create a word defined as “purified spirit” or “enlightened attitude” within Japanese martial arts.
洗心 is one of the five spirits of the warrior (budo) and is often used as a Japanese martial arts tenet. Under that context, it's often defined as a spirit that protects and harmonizes the universe. Senshin is a spirit of compassion that embraces and serves all humanity and whose function is to reconcile discord in the world. It holds all life to be sacred. It is the Buddha mind.
This title will only be familiar to Japanese who practice certain martial arts. Others may not recognize this word at all.
洗心 does not show up as a word in too many Chinese dictionaries, but it can be read and has the same meaning in Chinese.
![]() There is an issue with the first character. The original, and probably most correct version is shown above. However, many dojo documents and other sources have used a more simple first character. Arguments ensue about which version is correct. If you want to be correct in the Japanese language, use the "Select and Customize" button above. If you want to match the Kanji used by your dojo, click the Kanji shown to the right. There is a slightly different meaning with this first character which means before, ahead, previous, future, precedence.
There is an issue with the first character. The original, and probably most correct version is shown above. However, many dojo documents and other sources have used a more simple first character. Arguments ensue about which version is correct. If you want to be correct in the Japanese language, use the "Select and Customize" button above. If you want to match the Kanji used by your dojo, click the Kanji shown to the right. There is a slightly different meaning with this first character which means before, ahead, previous, future, precedence.
Fate / Opportunity / Chance
The Buddhist idea of Fate
因緣 is the Buddhist concept of a chance meeting or an opportunity that presents itself by fate.
Sometimes this is used to describe a cosmic chain of events or cause and effect.
It also is used to describe predestined relationships between people - and sometimes married couples (although if you want one about marriage, try this: Fate / Destiny of Lovers.
因緣 can also be translated as origin, karma, destiny, affinity, connection, and relation. This all depends on context - seen alone on a wall scroll, this will be read with a “fate/chance” meaning by a Chinese person or a Korean person who can read Hanja.
The more complex definition of this word would be, “Direct causes and indirect conditions, which underlie the actions of all things.”
This concept is known as nidana in the original Sanskrit. Also sometimes presented as hetupratyaya (or “hetu and prataya”), which I believe is Pali.
Note: Japanese will tend to use this version of the second Kanji: ![]()
If you order this from the Japanese master calligrapher, expect that you’ll get this version. However, this word often carries a negative connotation in Japanese (bad things happen), as it is used that way in a certain Japanese idiom. Therefore, this may not be the best choice if Japanese is your target language.
See Also: Buddhism | Opportunity
Student
學生 is how to write “student” in Chinese, pre-WWII Japanese Kanji, and old Korean Hanja.
If you are a “student of life,” this might be an interesting wall scroll to hang in your reading room.
The first character means “study” or “learning.”
The second character means “life” or “birth.” Don't read too much into that second character unless you decide that this means “the birth of studies” or “the life of learning.” Everyone in China, Japan (and those who can read Hanja in Korea) will just read this word with the meaning of “student.”
If you put the character for “little” in front of this word, it becomes “elementary school student.” Prefixed with “middle,” it becomes “middle school student.” Prefixed with “big,” it becomes “university student” (though when these two characters for student are seen alone, it often suggests “university student”). The term “high school student” is written differently.
![]() There is a very common simplified version of the first character for this word. You will see this form in modern Japan and mainland China, Singapore, and other places. If you want this simplified version, please click on the character shown to the right instead of the "select and customize" button above.
There is a very common simplified version of the first character for this word. You will see this form in modern Japan and mainland China, Singapore, and other places. If you want this simplified version, please click on the character shown to the right instead of the "select and customize" button above.
Patience / Perseverance
忍 contains the ideas of patience, equanimity, perseverance, forbearance, and endurance. Alone, this single character can be a bit ambiguous or flexible. It can also mean to endure, to bear, to put up with, or to conceal. If you want to simply decide what this character means to you within the general meaning but keep it a mystery to others, this is a good choice.
If you want to be more direct, you may want to choose one of our other selections that mean perseverance or patience (you will see this character within those larger words/phrases).
There is a secondary meaning in Japanese since this is the first character of the word ninja.![]() Note that when writing this as Kanji, Japanese will tend to write it in the form shown to the right. If you select our Japanese master calligrapher, please expect this Kanji form (yes, it's just one stroke that is slightly different in location, crossing another stroke in the Japanese Kanji form).
Note that when writing this as Kanji, Japanese will tend to write it in the form shown to the right. If you select our Japanese master calligrapher, please expect this Kanji form (yes, it's just one stroke that is slightly different in location, crossing another stroke in the Japanese Kanji form).
See Also: Perseverance | Patience | Tenacious
Empress
皇后 is the title of empress/emperess, the female form of the emperor.
皇后 is used in Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and old Korean Hanja.
While the emperor's reign was for life, if he died, his wife would hold his power. In this case, a woman was the ultimate ruler of the greater part of East Asia (now China) until her death and the succession of the emperor's firstborn son to lead the empire. Numerous times in various Chinese dynasties, an empress took power in this way.
The first character means emperor by itself.
The second character alone can mean “wife of an emperor or king” (the first character clarifies that we are talking about an empress and not a queen). It can also mean sovereign or last offspring, depending on context.
Note: In some books, this word is translated as queen. While only incorrect if you get technical (because an empress is theoretically a higher level than a queen), the meaning is very similar.
皇后 is sometimes used for the title of queen, but more technically, this is the wife of the emperor (a higher level than a queen).
Lingering Mind
Zanshin
First off, 殘心 should only be used in the context of Japanese martial arts. In Chinese, it's a rather sad title (like a broken heart). In Chinese, the first character alone means destroyed, spoiled, ruined, injured, cruel, oppressive, savage, incomplete, or disabled. However, in Japanese, it's remainder, leftover, balance, or lingering.
The second character means heart, mind, soul, or essence in both languages.
殘心 is one of the five spirits of the warrior (budo) and is often used as a Japanese martial arts tenet. Under that context, places such as the Budo Dojo define it this way: The spirit of zanshin is the state of the remaining or lingering spirit. It is often described as a sustained and heightened state of awareness and mental follow-through. However, true zanshin is a state of focus or concentration before, during, and after the execution of a technique, where a link or connection between uke and nage is preserved. Zanshin is the state of mind that allows us to stay spiritually connected, not only to a single attacker but to multiple attackers and even an entire context; a space, a time, an event.
![]() In modern Japan (and Simplified Chinese), they use a different version of the first character, as seen to the right. Click on this character to the right instead of the button above if you want this modern Japanese version of lingering mind / zanshin.
In modern Japan (and Simplified Chinese), they use a different version of the first character, as seen to the right. Click on this character to the right instead of the button above if you want this modern Japanese version of lingering mind / zanshin.
Daoism / Taoism
Literally: The Way or Road
道 is the character “dao” which is sometimes written as “tao” but pronounced like “dow” in Mandarin.
道 is the base of what is known as “Taoism.” If you translate this literally, it can mean “the way” or “the path.”
Dao is believed to be that which flows through all things and keeps them in balance. It incorporates the ideas of yin and yang (e.g. there would be no love without hate, no light without dark, no male without female.)
The beginning of Taoism can be traced to a mystical man named
Lao Zi (604-531 BC), who followed, and added to the teachings of Confucius.
More about Taoism / Daoism here.
Note that this is pronounced “dou” and sometimes “michi” when written alone in Japanese but pronounced “do” in word compounds such as Karate-do and Bushido. It's also “do” in Korean.
Alternate translations and meanings: road, way, path; truth, principle province.
Important Japanese note: In Japanese, this will generally be read with the road, way, or path meaning. Taoism is not as popular or well-known in Japan so Daoist/Taoist philosophy is not the first thing a Japanese person will think of when they read this character.
See our Taoism Page
Immovable Mind
fudoshin
不動心 is one of the five spirits of the warrior (budo) and is often used as a Japanese martial arts tenet.
Under that context, places such as the Budo Dojo define it this way: An unshakable mind and an immovable spirit is the state of fudoshin. It is courage and stability displayed both mentally and physically. Rather than indicating rigidity and inflexibility, fudoshin describes a condition that is not easily upset by internal thoughts or external forces. It is capable of receiving a strong attack while retaining composure and balance. It receives and yields lightly, grounds to the earth, and reflects aggression back to the source.
Other translations of this title include imperturbability, steadfastness, keeping a cool head in an emergency, or keeping one's calm (during a fight).
The first two Kanji alone mean immobility, firmness, fixed, steadfastness, motionless, and idle.
The last Kanji means heart, mind, soul, or essence.
Together, these three Kanji create a title defined as “immovable mind” within the context of Japanese martial arts. However, in Chinese, it would mean “motionless heart,” and in Korean Hanja, “wafting heart” or “floating heart.”
Indomitable / Unyielding
不屈不撓 means “Indomitable” or “Unyielding.”
不屈不撓 is a long word by Chinese standards. At least, it is often translated as a single word into English. It's actually a proverb in Chinese.
If you want to break it down, you can see that the first and third characters are the same. Both mean “not” (they work as a suffix to make a negative or opposite meaning to whatever character follows).
The second character means “bendable.”
The last means “scratched” or “bothered.”
So this really means “Won't be bent, can't be bothered.” I have also seen it written as “Will not crouch, will not submit.” This comes from the fact that the second character can mean “to crouch” and the last can mean “to submit” (as in “to give in” such as “submitting to the rule of someone else”). This may explain better why these four characters mean “indomitable.”
Notes:
Some will translate this as “indomitable spirit”; however, technically, there is no character to suggest the idea of “spirit” in this word.
Other translations include indefatigability, indomitableness, or unremitting tenacity.
The first two characters can be stand-alone words in Chinese.
In Japanese, this is considered two words (with very similar meanings). It's more common to see the word order flipped to 不撓不屈 in Japanese.
The same characters are used in old Korean Hanja. Just like in Japanese, the words are swapped to 不撓不屈 creating a word pronounced “불요불굴” in Korean.
See 不撓不屈
Strong / Powerful / Force
強 is a character that means strong, strength, force, powerful, better, stubborn, and stiff (yes, all of this in one character).
This “strong” has less to do with physical strength and more to do with having a winning attitude, or just having the ability to win at something.
Note that most of the time, this character is pronounced “qiang” but when used with the meaning of stubborn, unyielding, or stiff, it is pronounced “jiang” in Chinese.
Also, sometimes “qiang” is used in modern Chinese to describe people that do crazy things (For example: Bicycling from Beijing to Tibet alone). I sometimes can be found outside my Beijing apartment wearing nothing but shorts and a tee-shirt while eating ice cream during a snow storm, just to hear my neighbors call me “qiang.” Maybe they mean “strong” but perhaps they are using the new meaning of “crazy strong.”
強 can also be a Chinese surname that romanizes as Jiang in the mainland or Chiang if from Taiwan.
強 is a valid Korean Hanja character with the same meaning but is mostly used in compound Korean words.
強 is used in Japanese (though normally in compound words). In Japanese, it has the same meaning but in some contexts can mean “a little more than...” or “a little over [some amount].” Most Japanese would read this as tough, strength, stiff, hard, inflexible, obstinate, or stubborn.
The variant 彊 is sometimes seen in older literature.
Daodejing / Tao Te Ching - Chapter 54
This is the Mawangdui version of Daodejing chapter 54.
By its virtue alone can one generation after another carry on the ancestral sacrifice.
Apply it to yourself, and by its power, you will be freed from dross.
Apply it to your household, and your household shall thereby have abundance.
Apply it to the village, and the village will be made secure.
Apply it to the kingdom, and the kingdom shall thereby be made to flourish.
Apply it to an empire, and the empire shall thereby be extended.
Therefore just as through oneself, one may contemplate Oneself;
So through the household one may contemplate the Household;
And through the village, one may contemplate the Village;
And through the kingdom, one may contemplate the Kingdom;
And through the empire, one may contemplate the Empire.
How do I know that the empire is so? By this.
What is firmly rooted cannot be pulled out;
What is tightly held in the arms will not slip loose;
Through this, the offering of sacrifice by descendants will never come to an end.
Cultivate it in your person, and its virtue will be genuine;
Cultivate it in the family, and its virtue will be more than sufficient;
Cultivate it in the hamlet, and its virtue will endure;
Cultivate it in the state, and its virtue will abound;
Cultivate it in the empire, and its virtue will be pervasive.
Hence look at the person through the person;
Look at the family through the family;
Look at the hamlet through the hamlet;
Look at the state through the state;
Look at the empire through the empire.
How do I know that the empire is like that?
By means of this.
Japanese Snapping Turtle / Chinese Soft Shell Turtle
鼈 refers to a species of turtle.

鼈 is Trionyx Sinensis.
鼈 refers to different turtles in different languages. See individual language notes below:
Japanese: 鼈 means “snapping turtle” or “mud turtle.” But rarely used as a single Kanji like this in Japanese.
Chinese: 鼈 means soft-shelled turtle. A specific species, Trionyx Sinensis is native to Asia.
In China, this species is related to the “wang ba,” a soft-shelled turtle sometimes known in English as a banjo turtle (due to its long neck, and general shape). Unfortunately, there is a word, “wang ba dan” which means the egg of this species of turtle. That term has come to mean “bastard” in Chinese (a turtle hatches from an abandoned egg, and does not know who his mother or father is). 鼈 is not a good selection for a wall scroll if your audience is Chinese.
In Korean, this character can be pronounced (though most Koreans would have to look it up in a dictionary). It has not been in common use in Korea for at least a few hundred years.
General notes: You may notice that the bottom half of this character is the same as some other turtle-related titles. That bottom half is actually an ancient character that means “toad.” ![]() Though not seen in this way today, most turtle-related characters hold the meaning of “a toad with a shell” in their ancient origin. That toad character is rarely used alone anymore but you can see what it looks like in the image to the right.
Though not seen in this way today, most turtle-related characters hold the meaning of “a toad with a shell” in their ancient origin. That toad character is rarely used alone anymore but you can see what it looks like in the image to the right.
Kirin / Giraffe / Mythical Creature
麒麟 is the title of a mythical beast of Asia.
The animal is thought to be related to the giraffe, and in some ways, it is a giraffe. However, it is often depicted with the horns of a dragon or deer and sometimes with the body like a horse, but many variations exist.
In Japanese, it is pronounced “Kirin” as in “Kirin Ichiban” beer.

Notes:
1. This is sometimes spelled as “kylin.”
2. In Japanese, this is the only Kanji word for giraffe. Therefore in Japan, this word needs context to know whether you are talking about the mythical creature or the long-necked giraffe of Africa.
3. Apparently, this was the first word used for regular giraffes in China (some were brought from Africa to China during the Ming Dynasty - probably around the year 1400). Though the mythical creature may have existed before, the name “qilin” was given to the “new giraffe.” This is because, more than 600 years ago, giraffes somewhat matched the mythical creature's description when Chinese people saw them for the first time. Later, to avoid such an ambiguous title, a three-character word was devised to mean a “giraffe of Africa.” The characters for “qilin” shown here are only for the mythological version in modern Chinese.
4. More information about the qilin / kirin from Wikipedia.
5. This creature is sometimes translated as the “Chinese Unicorn,” although it is generally portrayed with two horns. I think this is done more for the fantasy aspect of the unicorn and because most westerners don't know what a qilin or kirin is (this avoids a long explanation by the translator).
6. In Korean, this can mean kirin or simply giraffe (usually, the mythological creature is what they would think of when seeing these characters alone on a wall scroll).
These search terms might be related to Alone:
A Journey of 1000 Miles Begins With a Single Step
Alone / Solitary Existence
Alone With Only Your Shadow for Company
Fear Not Long Roads; Fear Only Short Ambition
Lonely
Lonely Soul / Lost Soul
Lonely Soul / Solitary
Not Only Can Water Float a Boat, It Can Sink It Also
Only God Can Judge Me
Only the Sleepless Know the Length of Night
Opportunity Knocks Only Once
Silent / Solitary
The Single Life
There is One Single Thread Binding My Way Together
You Are Only as Old as You Feel
You Only Live Once
The following table may be helpful for those studying Chinese or Japanese...
| Title | Characters | Romaji (Romanized Japanese) | Various forms of Romanized Chinese | |
| Alone Solitary Existence | 獨居 独居 | dokkyo / dokyo | dú jū / du2 ju1 / du ju / duju | tu chü / tuchü |
| Alone A Lone Person | 獨自一人 独自一人 | dú zì yì rén du2 zi4 yi4 ren2 du zi yi ren duziyiren | tu tzu i jen tutzuijen |
|
| Alone A Lone Person | 獨自 独自 | dokuji | ||
| Alone with only your shadow for company | 煢煢孑立形影相吊 茕茕孑立形影相吊 | qióng qióng jié lì xíng yǐng xiāng diào qiong2 qiong2 jie2 li4 xing2 ying3 xiang1 diao4 qiong qiong jie li xing ying xiang diao | ch`iung ch`iung chieh li hsing ying hsiang tiao chiung chiung chieh li hsing ying hsiang tiao |
|
| I Miss You | 我想你 | wǒ xiǎng nǐ wo3 xiang3 ni3 wo xiang ni woxiangni | wo hsiang ni wohsiangni |
|
| Desire Longing Craving | 慾 欲 | yoku | yù / yu4 / yu | yü |
| Lonely | 孤獨 孤独 | ko doku / kodoku | gū dú / gu1 du2 / gu du / gudu | ku tu / kutu |
| Independent Spirit | 獨立精神 独立精神 | dú lì jīng shén du2 li4 jing1 shen2 du li jing shen dulijingshen | tu li ching shen tulichingshen |
|
| Defense Defend | 防 | bou / bo | fáng / fang2 / fang | |
| Heart of Judo | 柔 | yawara | róu / rou2 / rou | jou |
| Independence | 獨立 独立 | dokuritsu | dú lì / du2 li4 / du li / duli | tu li / tuli |
| Phenomenon | 現象 现象 | genshou / gensho | xiàn xiàng xian4 xiang4 xian xiang xianxiang | hsien hsiang hsienhsiang |
| Laugh Smile | 笑 | e / shou / wa e / sho / wa | xiào / xiao4 / xiao | hsiao |
| Happiness Joy | 禧 | xǐ / xi3 / xi | hsi | |
| Lonely Soul Lost Soul | 孤魂 | gū hún / gu1 hun2 / gu hun / guhun | ku hun / kuhun | |
| Fight for a Goal | 爭 争 | zhēng / zheng1 / zheng | cheng | |
| Knight | 騎士 骑士 | ki shi / kishi | qí shì / qi2 shi4 / qi shi / qishi | ch`i shih / chishih / chi shih |
| Sangha Order of Monks | 僧 | sou / so | sēng / seng1 / seng | |
| Hitori | 独 | hitori / doku | dú / du2 / du | tu |
| Grandfather | 祖父 | so fu / sofu | zǔ fù / zu3 fu4 / zu fu / zufu | tsu fu / tsufu |
| Bravery Courage | 勇氣 勇气 / 勇気 | yuuki / yuki | yǒng qì / yong3 qi4 / yong qi / yongqi | yung ch`i / yungchi / yung chi |
| Perception of Knowledge | 知識 知识 | chishiki | zhī shi / zhi1 shi / zhi shi / zhishi | chih shih / chihshih |
| Strong Robust | 壯 壮 | sou / so | zhuàng / zhuang4 / zhuang | chuang |
| Hurricane Typhoon | 颱風 / 台風 台风 | tai fuu / taifuu / tai fu | tái fēng / tai2 feng1 / tai feng / taifeng | t`ai feng / taifeng / tai feng |
| Hurricane Typhoon | 颶風 飓风 | gufuu / gufu | jù fēng / ju4 feng1 / ju feng / jufeng | chü feng / chüfeng |
| Military Engineering | 工兵 | kouhei / kohei | gōng bīng gong1 bing1 gong bing gongbing | kung ping kungping |
| Power Strength | 力 | chikara / ryoku | lì / li4 / li | |
| Sitting Quietly | 靜坐 静坐 | sei za / seiza | jìng zuò / jing4 zuo4 / jing zuo / jingzuo | ching tso / chingtso |
| Color | 顏色 颜色 | kao iro / gan shoku kaoiro / ganshoku | yán sè / yan2 se4 / yan se / yanse | yen se / yense |
| Tenacious Tenacity | 頑強 顽强 | gan kyou / gankyou / gan kyo | wán qiáng wan2 qiang2 wan qiang wanqiang | wan ch`iang wanchiang wan chiang |
| Be Like Water | 像水一樣 | xiàng shuǐ yí yàng xiang4 shui3 yi2 yang4 xiang shui yi yang xiangshuiyiyang | hsiang shui i yang hsiangshuiiyang |
|
| Dharma The Law | 法 | hou / ho | fǎ / fa3 / fa | |
| Stone Rock | 石 | ishi | shí / shi2 / shi | shih |
| Ocean | 洋 | you / yo | yáng / yang2 / yang | |
| Great Expectations | 望 | bou / nozomi bo / nozomi | wàng / wang4 / wang | |
| Loyalty to Duty or Master | 忠 | chuu / chu | zhōng / zhong1 / zhong | chung |
| Darkness | 黑闇 黑暗 | hēi àn / hei1 an4 / hei an / heian | ||
| Inspire | 啟示 启示 | qǐ shì / qi3 shi4 / qi shi / qishi | ch`i shih / chishih / chi shih | |
| Honesty Fidelity | 信 | shin | xìn / xin4 / xin | hsin |
| Calm Tranquility | 安 | an | ān / an1 / an | |
| Brown | 褐 | katsu | hè / he4 / he | ho |
| Bat | 蝠 | fú / fu2 / fu | ||
| Justice Righteousness | 正義 正义 | sei gi / seigi | zhèng yì / zheng4 yi4 / zheng yi / zhengyi | cheng i / chengi |
| Kill Slaughter Murder Butcher | 殺 杀 | satsu | shā / sha1 / sha | |
| Opportunity | 機 机 | hata | jī / ji1 / ji | chi |
| Forgiveness (from the top down) | 容赦 | you sha / yousha / yo sha | róng shè / rong2 she4 / rong she / rongshe | jung she / jungshe |
| Best | 至 | shi | zhì / zhi4 / zhi | chih |
| Speed | 高速 | kousoku / kosoku | gāo sù / gao1 su4 / gao su / gaosu | kao su / kaosu |
| Good Health Healthy Vigor | 康 | kou / ko | kāng / kang1 / kang | k`ang / kang |
| North American Opossum Possum | 北美負鼠 北美负鼠 | běi měi fù shǔ bei3 mei3 fu4 shu3 bei mei fu shu beimeifushu | pei mei fu shu peimeifushu |
|
| Only the sleepless know the length of night | 不眠之夜長久交知人心 不眠之夜长久交知人心 | bù mián zhī yè cháng jiǔ jiāo zhī rén xīn bu4 mian2 zhi1 ye4 chang2 jiu3 jiao1 zhi1 ren2 xin1 bu mian zhi ye chang jiu jiao zhi ren xin | pu mien chih yeh ch`ang chiu chiao chih jen hsin pu mien chih yeh chang chiu chiao chih jen hsin |
|
| Vampire | 吸血鬼 | kyuu ketsu ki kyuuketsuki kyu ketsu ki | xī xuě guǐ xi1 xue3 gui3 xi xue gui xixuegui | hsi hsüeh kuei hsihsüehkuei |
| Listen | 聽 听 / 聴 | chou / ki / cho / ki | tīng / ting1 / ting | t`ing / ting |
| Mantis Praying Mantis | 螳螂 / 蟷螂 螳螂 | tou rou / tourou / to ro | táng láng tang2 lang2 tang lang tanglang | t`ang lang tanglang tang lang |
| Wellness | 身體健康 身体健康 | shin tai ken kou shintaikenkou shin tai ken ko | shēn tǐ jiàn kāng shen1 ti3 jian4 kang1 shen ti jian kang shentijiankang | shen t`i chien k`ang shentichienkang shen ti chien kang |
| Peace of Mind | 和平 | wa hei / wahei | hé píng / he2 ping2 / he ping / heping | ho p`ing / hoping / ho ping |
| Adventure | 探險 探险 / 探険 | tanken | tàn xiǎn / tan4 xian3 / tan xian / tanxian | t`an hsien / tanhsien / tan hsien |
| Mercy Compassion Love | 慈 | ji | cí / ci2 / ci | tz`u / tzu |
| Tooth for a tooth | 以牙還牙 以牙还牙 | yǐ yá huán yá yi3 ya2 huan2 ya2 yi ya huan ya yiyahuanya | i ya huan ya iyahuanya |
|
| Joushiki Wo Koeru | 常識を超える | jou shiki wo ko e ru joushikiwokoeru jo shiki wo ko e ru | ||
| Reiki - Master Symbol | 大光明 | dai kou myou daikoumyou dai ko myo | dà guāng míng da4 guang1 ming2 da guang ming daguangming | ta kuang ming takuangming |
| Religious Devotion Faith in God Religious Faith | 信仰 | shin kou / shinkou / shin ko | xìn yǎng / xin4 yang3 / xin yang / xinyang | hsin yang / hsinyang |
| Happy Laughter Cheerful Bliss | 樂 / 楽 乐 | raku | lè / le4 / le | |
| Lost Dazed and Confused | 迷 | mei | mí / mi2 / mi | |
| Woman | 巾幗 巾帼 | jīn guó / jin1 guo2 / jin guo / jinguo | chin kuo / chinkuo | |
| Gaman | 我慢 | ga man / gaman | wǒ màn / wo3 man4 / wo man / woman | |
| Heart Mind Spirit | 心 | kokoro | xīn / xin1 / xin | hsin |
| The Saint | 聖 圣 | sei | shèng / sheng4 / sheng | |
| Cooperation Collaboration | 協作 协作 | kyou saku / kyousaku / kyo saku | xié zuò / xie2 zuo4 / xie zuo / xiezuo | hsieh tso / hsiehtso |
| Spirit Spiritual Essence | 神 | shin / kami | shén / shen2 / shen | |
| Wolf | 狼 | okami | láng / lang2 / lang | |
| Che Guevara | 切格瓦拉 | qiè gé wǎ lā qie4 ge2 wa3 la1 qie ge wa la qiegewala | ch`ieh ko wa la chiehkowala chieh ko wa la |
|
| Dynasty | 代 | dai | dài / dai4 / dai | tai |
| Diligence | 勤 | kin | qín / qin2 / qin | ch`in / chin |
| Koi Fish Nishiki Goi | 錦鯉 锦鲤 | nishiki goi nishikigoi | jǐn lǐ / jin3 li3 / jin li / jinli | chin li / chinli |
| Purified Spirit Enlightened Attitude | 洗心 先心 | sen shin / senshin | xǐ xīn / xi3 xin1 / xi xin / xixin | hsi hsin / hsihsin |
| Fate Opportunity Chance | 因緣 因缘 / 因縁 | in nen / innen | yīn yuán / yin1 yuan2 / yin yuan / yinyuan | yin yüan / yinyüan |
| Student | 學生 学生 | gakusei | xué shēng xue2 sheng1 xue sheng xuesheng | hsüeh sheng hsüehsheng |
| Patience Perseverance | 忍 | nin | rěn / ren3 / ren | jen |
| Empress | 皇后 | kou gou / kougou / ko go | huáng hòu huang2 hou4 huang hou huanghou | |
| Lingering Mind | 殘心 残心 | zan shin / zanshin | cán xīn / can2 xin1 / can xin / canxin | ts`an hsin / tsanhsin / tsan hsin |
| Daoism Taoism | 道 | michi / -do | dào / dao4 / dao | tao |
| Immovable Mind | 不動心 | fu dou shin fudoushin fu do shin | ||
| Indomitable Unyielding | 不屈不撓 不屈不挠 | fu kutsu fu tou fukutsufutou fu kutsu fu to | bù qū bù náo bu4 qu1 bu4 nao2 bu qu bu nao buqubunao | pu ch`ü pu nao puchüpunao pu chü pu nao |
| Strong Powerful Force | 強 强 | kyou / kyo | qiáng / qiang2 / qiang | ch`iang / chiang |
| Daodejing Tao Te Ching - Chapter 54 | 善建者不拔善抱者不脫子孫以祭祀不絕修之身其德乃真修之家其德有余修之鄉其德乃長修之國其德乃夆修之於天下其德乃博以身觀身以家觀家以鄉觀鄉以邦觀邦以天下觀天下吾何以知天下然茲以此 善建者不拔善抱者不脱子孙以祭祀不绝修之身其德乃真修之家其德有余修之乡其德乃长修之国其德乃夆修之于天下其德乃博以身观身以家观家以乡观乡以邦观邦以天下观天下吾何以知天下然兹以此 | shàn jiàn zhě bù bá shàn bào zhě bù tuō zǐ sūn yǐ jì sì bù jué xiū zhī shēn qí dé nǎi zhēn xiū zhī jiā qí dé yǒu yú xiū zhī xiāng qí dé nǎi zhǎng xiū zhī guó qí dé nǎi féng xiū zhī yú tiān xià qí dé nǎi bó yǐ shēn guān shēn yǐ jiā guān jiā yǐ xiāng guān xiāng yǐ bāng guān bāng yǐ tiān xià guān tiān xià wú hé yǐ zhī tiān xià rán zī yǐ cǐ shan4 jian4 zhe3 bu4 ba2 shan4 bao4 zhe3 bu4 tuo1 zi3 sun1 yi3 ji4 si4 bu4 jue2 xiu1 zhi1 shen1 qi2 de2 nai3 zhen1 xiu1 zhi1 jia1 qi2 de2 you3 yu2 xiu1 zhi1 xiang1 qi2 de2 nai3 zhang3 xiu1 zhi1 guo2 qi2 de2 nai3 feng2 xiu1 zhi1 yu2 tian1 xia4 qi2 de2 nai3 bo2 yi3 shen1 guan1 shen1 yi3 jia1 guan1 jia1 yi3 xiang1 guan1 xiang1 yi3 bang1 guan1 bang1 yi3 tian1 xia4 guan1 tian1 xia4 wu2 he2 yi3 zhi1 tian1 xia4 ran2 zi1 yi3 ci3 shan jian zhe bu ba shan bao zhe bu tuo zi sun yi ji si bu jue xiu zhi shen qi de nai zhen xiu zhi jia qi de you yu xiu zhi xiang qi de nai zhang xiu zhi guo qi de nai feng xiu zhi yu tian xia qi de nai bo yi shen guan shen yi jia guan jia yi xiang guan xiang yi bang guan bang yi tian xia guan tian xia wu he yi zhi tian xia ran zi yi ci | shan chien che pu pa shan pao che pu t`o tzu sun i chi ssu pu chüeh hsiu chih shen ch`i te nai chen hsiu chih chia ch`i te yu yü hsiu chih hsiang ch`i te nai chang hsiu chih kuo ch`i te nai feng hsiu chih yü t`ien hsia ch`i te nai po i shen kuan shen i chia kuan chia i hsiang kuan hsiang i pang kuan pang i t`ien hsia kuan t`ien hsia wu ho i chih t`ien hsia jan tzu i tz`u shan chien che pu pa shan pao che pu to tzu sun i chi ssu pu chüeh hsiu chih shen chi te nai chen hsiu chih chia chi te yu yü hsiu chih hsiang chi te nai chang hsiu chih kuo chi te nai feng hsiu chih yü tien hsia chi te nai po i shen kuan shen i chia kuan chia i hsiang kuan hsiang i pang kuan pang i tien hsia kuan tien hsia wu ho i chih tien hsia jan tzu i tzu |
|
| Japanese Snapping Turtle Chinese Soft Shell Turtle | 鼈 | suppon / supon | biē / bie1 / bie | pieh |
| Kirin Giraffe Mythical Creature | 麒麟 | kirin | qí lǐn / qi2 lin3 / qi lin / qilin | ch`i lin / chilin / chi lin |
| In some entries above you will see that characters have different versions above and below a line. In these cases, the characters above the line are Traditional Chinese, while the ones below are Simplified Chinese. | ||||
Successful Chinese Character and Japanese Kanji calligraphy searches within the last few hours...



























































































