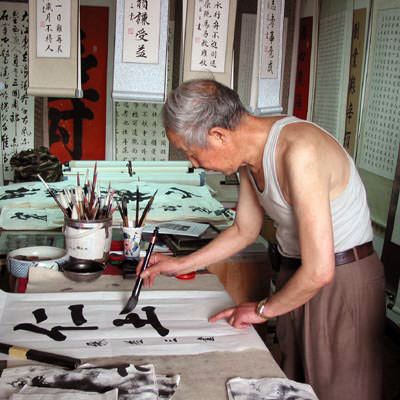
Many custom options...
And formats...

Simplified in Chinese / Japanese...
Buy a Simplified calligraphy wall scroll here!
Personalize your custom “Simplified” project by clicking the button next to your favorite “Simplified” title below...
1. Simplicity
4. Doctor
5. Qian
6. France
7. Shotokan
9. Sakuragi
10. Kaylee
11. France
12. English / Briton / Person from England
13. Gemini
14. Hitori
15. Ford
16. Honor
17. Empire
18. Gemini
19. Mumonkan / The Gateless Gate
20. Navy SEALS
21. Twins
22. Doctor
24. The Holy Trinity
26. Sesshin
28. Seikaze
29. Manga
32. Aiki O'Kami
33. Kindheartedness / Benevolence / Humanity
34. Opportunity
37. Shiatsu-Do
38. Reincarnation
39. Sushi
40. Independent Spirit / Independent Heart
41. Respect
43. Tang Soo Do / Tang Hand Way
44. Banzai / Wansui
45. Kyojitsu: Falsehood and Truth
46. Taido
47. Banzai
48. Reiki
49. Hapkido
50. Guanxi
Simplicity
簡 expresses the idea of something simple or the essence of simplicity in life in Chinese.
This can also refer to a simple slip of bamboo for taking notes or writing a letter (especially in Korean Hanja).
Technically this is a word meaning simplicity and brevity in Japanese but it's rarely used in modern Japanese. Therefore, you should probably only select this character if your audience is Chinese.
See Also: Brevity
Smooth and Steady
平穩 can also be translated as calmness, quietness, or quietude and is used in Chinese and Korean.
The version shown here would be considered the ancient Japanese form. The second character has been simplified in Japan (the same simplified form is used in mainland China, except for calligraphy).
Please include special instructions with your order if you want the simplified form of that second character. Both forms can be universally read.
See Also: Smooth Sailing
Physical Strength
体力 means “physical strength” or “physical power.”
The first character was first simplified in Japan. Later, that simplified version became the standard in mainland China. Just in case you want this version, it is offered here. I suggest it if your audience is Japanese. Most Chinese know the older traditional version, which looks like 體力.
体力 can also be defined: stamina; endurance; physical strength; resilience; resistance to disease; clout; stability.
Doctor
醫生 is the title used to refer to medical doctors or physicians in China.
Note: Sometimes, this same term is used in Korean, but not common.
The meaning is close to “healer [of] life” as the first character, 醫, can mean medicine, the healing art, healing, curing, medical, to cure, or to treat. The second character, 生, means birth or life.
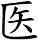
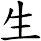 In Japan, they use a simplified version of the first character (医生 is also used as the Simplified Chinese version of Doctor). If you want this version, please click the characters to the right instead of the button above.
In Japan, they use a simplified version of the first character (医生 is also used as the Simplified Chinese version of Doctor). If you want this version, please click the characters to the right instead of the button above.
Qian
This can be the Chinese ancient surname Gan or current surname Qian. In Japanese, it can be the surname Nukui, Susumu, Ken, Kan, Kawaki, Kawai, Inute, or Inui.
The meaning of this character varies a lot depending on context. These meanings include dry, clean, foster, adoptive, heaven, male, masculine, enduring, or continual.
The “Gan” version of this character was converted to Simplified Chinese as 干 in 1965. However, the “Qian” pronunciation is not associated with 干. Though to add to the confusion, there is an unrelated Simplified Chinese character 千 that romanizes as “Qian” and is also a surname.
France
Shotokan
松濤館 are the Kanji characters that make up the title for Shotokan.
This should be considered a Japanese-only title. It does make sense and is pronounceable in Chinese and Korean but only as a title for a building (perhaps a martial arts hall) surrounded by pine trees. Also, the first two characters were simplified in both Japanese and Chinese. The third character was simplified in Chinese but not Japanese.
Upon request, we can offer the fully traditional Chinese version but be sure you know what you are asking for.
Note: This would be understood in Chinese and Korean Hanja by a person from those cultures who is familiar with martial arts and various schools of Japanese karate.
Shotokan Karate-Do
鬆濤館空手道 art the Japanese Kanji that make up the title for Shotokan Karate.
This should be considered a Japanese-only title. It does make sense and is pronounceable in Chinese and Korean but only as a title for a building (perhaps a martial arts hall) surrounded by pine trees - followed by the characters for “The empty hand method” (kong shou dao / Karate-do). Also, the first two characters were simplified in both Japanese and Chinese. The third character was simplified in Chinese but not Japanese.
Upon request, we can offer the fully traditional Chinese version but be sure you know what you are asking for.
Note: This would be understood in Chinese and Korean Hanja by a person from those cultures familiar with martial arts and various schools of Japanese karate.
Sakuragi
Kaylee
France
English / Briton / Person from England
Gemini Zodiac Symbol / Sign
雙子座 is the Japanese way to write Gemini (twins) from western astrology.
This also happens to be the Simplified Chinese version of this title - however, I recommend the Traditional Chinese version if your audience is Chinese.
See Also: Chinese Zodiac
Hitori
This is the Japanese given name 独 which romanizes as Hitori or Doku.
Originally this was written as 獨 but was simplified/modernized in Japan at some point.
独 can also be an abbreviation for Germany.
The actual meaning is alone, independent, single, sole, only, or solitary.
This is also a Simplified Chinese character, but most Chinese calligraphers would prefer to write the Traditional Chinese of 獨 instead of 独.
Ford
Honor
(Modern Japanese version)
名譽 is a version of honor that is about having or earning the respect of others and about your reputation.
It is the status of being worthy of honor (not to be confused with doing honorable things or specific actions - see our other “honor” listing for that).
![]() Both modern Japanese and modern mainland Chinese use the same simplified version of the second character of honor. You can make a special request for the traditional second character as shown to the right (just click on that character to the right of you want to order that version). Before WWII, both Japan and China used the traditional form but modern Japanese and Chinese use this simplified form. Koreans still use the traditional form when they are not writing in their modern Hangul glyphs.
Both modern Japanese and modern mainland Chinese use the same simplified version of the second character of honor. You can make a special request for the traditional second character as shown to the right (just click on that character to the right of you want to order that version). Before WWII, both Japan and China used the traditional form but modern Japanese and Chinese use this simplified form. Koreans still use the traditional form when they are not writing in their modern Hangul glyphs.
This is also a virtue of the Samurai Warrior
See our page with just Code of the Samurai / Bushido here
Empire
帝國 is a Japanese and Chinese word that means empire or imperial.
Note: In modern Japan, they tend to write 帝国 instead of 帝國. Let us know if you want the modern Japanese (which is also the Simplified Chinese) version.
Gemini Zodiac Symbol / Sign
雙子座 is the Chinese way to write Gemini (twins) of western astrology.
This was also the version used in Japan until they simplified the first Kanji to 双 after WWII. If you need the modern Japanese 双子座 instead of the older 雙子座, just let me know when you place your order.
See Also: Chinese Zodiac
Mumonkan / The Gateless Gate
無門関 is the specifically Japanese title for “The Gateless Barrier.”
This has both direct meaning and is the title of a 13th-century collection of koans, compiled by Zen Master Mumon (actually a Chinese Chan Master known as Wumen in China).
The original title is 無門關, but the last Kanji was simplified to 関 in modern Japan.
Twins
Doctor
醫師 is the title used to refer to medical doctors or physicians in old Korean Hanja.
Notes:
Also means “doctor” in Chinese but is not the most commonly used title.
醫師 is the ancient/traditional form of doctor in Japanese (they simplified the first character to 医 in Japan after WWII).
Serenity / Tranquility
靜穏 is a Japanese-specific way to express “serenity” or “tranquility.”
Notes: The second Kanji is not a Chinese character - it was morphed or developed in Japan after Chinese characters were absorbed into the Japanese language during the 5th century.
The first character is slightly-simplified from the original Chinese form but still recognizable.
See Also: Peace
The Holy Trinity
三位一體 is the Chinese and old Korean way to write Holy Trinity.
This would be understood in Japanese as well, but they tend to write it with the last character simplified like 三位一体 in modern Japan.
This can be translated literally as “Three Thrones, One Body.”
Asian Christians will understand this as the Trinity, God the Father, the Son, and the Holy Spirit.
The Gateless Gate
無門關 is the ancient title for “The Gateless Barrier.”
This has both direct meaning and is the title of a 13th-century collection of koans, compiled by a Chinese Chan Master known as Wumen in China (known in Japan as Zen Master Mumon).
While this is the original title, you may see this written as 無門関 in Japan, where the last character, 關, was simplified to 関 after 1945.
Sesshin
接心 is a Japanese Buddhist term meaning concentration or a period of intensive zazen.
While 接心 is the most common way to write this, other variants include 攝心 (Traditional Chinese), 摂心 (alternate Japanese), and 摄心 (Simplified Chinese). If you need any of these alternate forms, just let me know and I will set it up with the calligrapher for you.
While this is a Japanese term, it will be recognized by most Chinese folks at a Japanese Buddhist term and they will pronounce it as “jiē xīn” in Mandarin.
Kingdom of Heaven
天国 is the same meaning and pronunciation as our other entry for “Kingdom of Heaven,” but the second character was simplified in Japan and mainland China to this version.
Choose the appearance that you like best (they will be somewhat universally understood - as most people are aware of this simplification in places where they still use all traditional characters - such as Taiwan and Hong Kong). You can consider the other version to be the “ancient version.”
Seikaze
静風 means quiet wind, silent wind, or serenity wind.
This can also be a given name often pronounced Seifū in Japanese and can also be pronounced Shizukaze in Japanese.
Some might also write this as 靜風 with a slight difference in the first character.
In Simplified Chinese, it's 静风.
This word is more commonly used in Japanese than Chinese, but it can be read in both languages with the same meaning.
Manga
漫画 is the Japanese word for cartoon, comic, caricature, or comic strip.
The older traditional form is 漫畫 and is sometimes still used in Taiwan and China (and occasionally in Japan) when referring specifically to Japanese comics.
You'll see the same 漫画 used in Mainland China as well since 画 is not just the modern Japanese form but also the Simplified Chinese version of the original 畫.
Courtesy / Etiquette
In Japanese, 礼儀 means “manners,” “courtesy,” or “etiquette.”
This also clearly means etiquette in Chinese, though the first Japanese Kanji has been “modernized” and happens to be the same as the modern Simplified Chinese version. Therefore, this word will be understood by both Japanese and Chinese people but best if your audience is mostly Japanese (Chinese people would generally prefer the ancient Traditional Chinese version).
Shakyamuni / The Buddha
釈迦 is the way to write Shakyamuni in Japanese.
It's just two Kanji, the first is a simplified version of the one used in Chinese for Shakyamuni, and the second one is identical to the Chinese.
This refers to the Buddha (Siddhartha Gautama, 563 BCE-483 BCE) also known as Sakyamuni and Gautama Buddha.
This has a very good meaning in Japanese but is an odd selection for a wall scroll. It appears here more for reference.
Aiki O'Kami
This is the Japanese martial arts Aiki O'Kami.
The Aiki (合気/合氣) means harmonious energy. While Okami or O'kami (大神) means great spirit.
You will usually see this title written as 合氣大神, though in modern Japanese (after 1945) the second character, 氣, was simplified to 気 in Japan (and 气 in China). I suggest you use 合氣大神, but please let me know when you order if you would prefer 合気大神 instead.
Kindheartedness / Benevolence / Humanity
仁德 is a word that can be translated as love, kindheartedness, benevolence, and humanity.
The first character means benevolence by itself.
The second character means virtue or morality.
Japanese note: The second Kanji of this word has been slightly simplified (one tiny horizontal stroke removed). It is still readable for Japanese but if you select our Japanese calligrapher, expect that stroke to be missing on your wall scroll.
Opportunity
機会 is a common way to express “opportunity” in Japanese.
The first character means “chance,” and the second can be translated as “meeting.”
So in Japanese business, a “chance meeting” represents a real “opportunity.”
Note that this also means opportunity in Chinese, but it's more an oral or informal word in Mandarin. Also, the second Kanji is the same as the simplified version of the hui Chinese character.
Courtesy / Etiquette
In Chinese, old Korean Hanja, and old Japanese Kanji, 禮儀 means “etiquette” or “courtesy.”
You'll also find a Japanese entry on our website, which uses a modern/simplified first Kanji. The characters shown here compose the best choice if your audience is Chinese or Korean - but also acceptable if you want an ancient-style Japanese scroll (in modern Japanese, it has the same pronunciation, but is written 礼儀).
Note: This can also be translated as propriety, decorum, or formality.
Kingdom of Heaven
天國 is the very Christian way to refer to the “Kingdom of Heaven” in Chinese, old Korean, and Japanese. 天國 is also the translation for “paradise.”
The first character means “Heaven.” The second character means “kingdom” but, in modern times, has been extended to mean “country” (but no one will translate this particular character combination as “Heaven Country”). 天國 is the ancient version of this word, as in modern times (after WWII), the second character was simplified in mainland China and Japan.
Shiatsu-Do
指圧道 is the title for Shiastu-Do, the Japanese way of finger pressure.
Shitsu-Do is about applying special finger pressure to points on the body thought to be connected to pathways called “meridians.” Shiatsu is a healthful way to get your 気 or 氣 (ki energy) flowing properly.
Note: This title can also be written in the older 指壓道 form (just the middle character has an ancient/traditional form used before WWII).
You might even see 指压道 which uses the Simplified Chinese form of the second character.
Reincarnation (Buddhism)
轉世 is the Buddhist idea of reincarnation or transmigration.
Other definitions of this term: “Attainer of Nirvana from within the desire realm,” “A practitioner who enters directly into Nirvana from the desire realm, without traversing the form and formless realms. One of the 27 kinds of Hinayana sages,” or simply, “to return again to this life.”
轉世 is also a Japanese title, but the first Kanji was slightly simplified after WWII. Just let us know if you want the modern Japanese version when you order.
Sushi
Got a 寿司/sushi restaurant and need an appropriate wall scroll? Or maybe you love sushi enough to have it on your wall. This sushi calligraphy scroll is for you.
Note that the written characters for sushi are the same in Chinese and Japanese. However, the first character is actually a modern Japanese / Simplified Chinese, so in some cases, it will be written differently in Taiwan, Hong Kong, and some older Japanese sushi restaurants where you might see 壽司 instead of 寿司.
Independent Spirit / Independent Heart
獨立心 means independent spirit or independent heart in Japanese.
The first two characters mean independent or independence. The third character means spirit, heart, or mind.
獨立心 is a Japanese term, although Chinese people could guess the meaning (the characters make sense individually in Chinese but are not often used this way). Also, the first character would be written 獨 in Traditional Chinese versus 独 which is the Simplified Chinese and modern Japanese version.
Respect
Politeness, Gratitude and Propriety
礼 is one of the five tenets of Confucius.
Beyond respect, 礼 can also be translated as propriety, good manners, politeness, rite, worship, or an expression of gratitude.
We show respect by speaking and acting with courtesy. We treat others with dignity and honor the rules of our family, school, and nation. Respect yourself, and others will respect you.
 Please note that Japanese use this simplified 礼 version of the original 禮 character for respect. 礼 also happens to be the same simplification used in mainland China. While 禮 is the traditional and original version, 礼 has been used as a shorthand version for many centuries. Click on the big 禮 character to the right if you want the Traditional Chinese and older Japanese versions.
Please note that Japanese use this simplified 礼 version of the original 禮 character for respect. 礼 also happens to be the same simplification used in mainland China. While 禮 is the traditional and original version, 礼 has been used as a shorthand version for many centuries. Click on the big 禮 character to the right if you want the Traditional Chinese and older Japanese versions.
This is also a virtue of the Samurai Warrior
See our page with just Code of the Samurai / Bushido here
See Also: Confucius
Zen / Chan / Meditation
...as in Zen Buddhism
First, let's correct something: The Japanese romanization for this character, “Zen” has penetrated the English language. In English, it's almost always incorrectly used for phrases like “That's so zen.” Nobody says, “That's so meditation” - right? As the title of a sect, this would be like saying, “That's so Baptist!"
禪 by itself just means “meditation.” In that context, it should not be confined to use by any one religion or sect.
Regardless of the dictionary definition, more often than not, this character is associated with Buddhism. And here is one of the main reasons:
Zen is used as the title of a branch of Mahayana Buddhism, which strongly emphasizes meditation practice.
However, it should be noted that Buddhism came from India, and “Chan Buddhism” evolved and developed in medieval China. The Chinese character “Chan” was eventually pronounced as “Zen” in Japanese. Chan Buddhists in China have much in common with Zen Buddhists in Japan.
More about the history of Zen Buddhism here.
Please also note that the Japanese Kanji character for Zen has evolved a little in Japan, and the two boxes (kou) that you see at the top of the right side of the character have been replaced by three dots with tails.
 The original character would still be generally understood and recognized in Japanese (it's considered an ancient version in Japan) but if you want the specifically modern Japanese version, please click on the zen Kanji to the right. Technically, there is no difference between the Tensho and Reisho versions of Zen since they are ancient character styles that existed long before Japan had a written language.
The original character would still be generally understood and recognized in Japanese (it's considered an ancient version in Japan) but if you want the specifically modern Japanese version, please click on the zen Kanji to the right. Technically, there is no difference between the Tensho and Reisho versions of Zen since they are ancient character styles that existed long before Japan had a written language.![]() There is also an alternate/shorthand/simplified Chinese version, which has two dots or tails above the right-side radical. This version is also popular for calligraphy in China. If you want this version, just click the character to the right.
There is also an alternate/shorthand/simplified Chinese version, which has two dots or tails above the right-side radical. This version is also popular for calligraphy in China. If you want this version, just click the character to the right.
Further notes: Zen is just one of seven sects of Buddhism practiced in Japan. The others are 律 Ritsu (or Risshū), 法相 Hossō, 論 Sanron 華嚴 Kegon, 天台 Tendai, and 眞言 Shingon.
Tang Soo Do / Tang Hand Way
唐手道 is the alternate title for Karate-do.
This title uses a character, 唐, which represents the Tang Dynasty of China. Thus, this is often translated as the “Tang Hand Way” or incorrectly, “Tang Fist Way.”
I have also seen some call it “China Hand Way.”
Many in Korea refer to and romanize these characters as “Tang Soo Do” (당수도) where these characters refer to a kind of Korean style of Karate.
There is not a lot of information on this title but some believe that a simplified form of Kung Fu that started in China and ended up very popular in Japan used this title initially. It was later changed in Japan to a different Karate title which means “Empty Hand” (as in, without weapons).
Note: When used in Korean, this is pronounced 당수도. This title is often romanized as “Tang Soo Do,” “Tangsudo,” “Dang Su Do,” or “Dangsudo.” The last two romanizations on that list are the official Korean government romanization, though martial arts schools tend to use other non-standard versions.
Banzai / Wansui
Old Japanese / Traditional Chinese & Korean
萬歲 is the traditional Chinese, Korean Hanja, and ancient Japanese way of writing banzai.
In modern times, the first character was simplified in Japan and China. So you might want to select the other entry for universal readability.
While it has become a popular, if not an odd, thing to scream as you jump out of an airplane (preferably with a parachute attached), banzai is actually a very old Asian way to say “hooray.” The Japanese word “banzai” comes from the Chinese word “wan sui,” which means “The age of 10,000 years.” It is actually a wish that the Emperor or the Empire live that long.
Imagine long ago when the Emperor made a rare public appearance. 萬歲 is what all people would yell to their leader in respect.
So if you like it as a hooray, or you want to wish someone that they live for 10,000 years, this is the calligraphy for you.
Other translations include Cheers! (not the drinking kind), hurrah!, long live [name]!, and congratulations!
To other things with banzai in their names, I am still waiting for the promised sequel to Buckaroo Banzai.
Notes: Sometimes people confuse banzai with bonsai. A bonsai is a miniature tree. They have nothing to do with each other.
Kyojitsu: Falsehood and Truth
虚実 is a Japanese word that means “falsehood [and] truth” or “fiction [and] fact.”
This concept is used in warfare, gameplay, and martial arts strategies. 虚実 can be a strategy of real and/or deceptive moves. This gets to some Sun Tzu Art of War stuff where in warfare a strategic move is either a real and serious move or it is a deceptive blow.
Let's explore each character in more depth:
虚 was originally written 虛 (there is a very subtle difference in the strokes at the bottom of the character) and means unpreparedness, falsehood, emptiness, void, abstract theory, empty or unoccupied, diffident or timid, false, humble or modest, virtual, or in vain.
In the Buddhist context, 虛 represents the Pali/Sanskrit word “śūnya,” meaning empty, vacant, unreal, unsubstantial, untrue, space, humble, or in vain.
In ancient Eastern/Chinese astronomy, 虛 represents the “Emptiness” constellation (one of the 28 mansions in the sky).
実 was originally 實 in Chinese (they currently write it as 实 in Simplified Chinese) with the meaning, truth, reality, sincerity, honesty, fidelity, and substance.
The Buddhist context is similar, adding real, true, honest, really, solid, definitely, sincere, solid, fixed, full, to fill, fruit, kernel, verily, in fact, the supreme fact, or ultimate reality to the definition.
Taido
Taidō (The Way of the Body) is a style of Karate practiced in Japan and popular worldwide.
Taidō or 躰道 traces a lineage from Genseiryū (玄制流), which came from Shuri-te (首里手), one of the original martial arts schools of ancient Okinawa.
The first character 躰 is a variant of the original Chinese character 體. In modern Japan, they tend to use 体, a more simple character form. 体 is also the modern Simplified Chinese form of 體.
The 躰 character is correct for this 躰道 martial arts title. But it can be confusing with so many variants out there, not to mention other homophonic Japanese words that also romanize as Taidō or Taidou.
To have a bit more fun with this 躰 character, it has a 身 radical on the left, which sets it apart. The meaning doubles up on the “body” as 身 (shin) is a character that also means body in Japanese and Chinese. On the right is 本, which often means root, stem, origin, source, or fundamental (but can also mean “book” in some contexts). This has deviated from the original 體 which was 骨 (bone) + 豊 (vessel). Hence, the body was your “bone vessel” in ancient Asia.
The meaning of 躰, as well as 體 and 体, is usually translated as the body. When related to the physical body, it can also refer to the torso, trunk, build, physique, or the constitution of a person. As an extension of this, it can also refer to someone's health (good body = good health).
However, depending on the context, it can encompass other meanings such as form, style, system, experience, aspect, corpus, corporeal, substance, or essentials.
The second character, 道, is recognized and well-known as the “Way” and is the same “do” as in Karate-do or Aikido.
Banzai
Modern Japanese Version
万歲 is the modern Japanese way to write banzai.
We've made two almost identical entries for this word, with just a variation on the first character. In the last century, 萬 was simplified to 万 in Japan and China. The new generation will expect it to be written as 万 but the old generation can still read the more traditional 萬 form. You must make your determination as to what version is best for you. If your audience is mostly Japanese, I suggest 万歲.
While it has become a popular, if not an odd, thing to scream as you jump out of an airplane (preferably with a parachute attached), banzai is actually a very old Asian way to say “hooray.” The Japanese word “banzai” comes from the Chinese word “wan sui” which means “The age of 10,000 years.” It is actually a wish that the Emperor or the Empire live that long.
Imagine long ago when the Emperor made a rare public appearance. This is what all of the people would yell to their leader in respect.
So if you like it as a hooray, or you want to wish someone that they live for 10,000 years, this is the calligraphy for you.
To other things with banzai in their names, I am still waiting for the promised sequel to Buckaroo Banzai.
Other translations: hurrah, long life, congratulations, cheers, live long.
Notes: Sometimes people confuse banzai with bonsai. A bonsai is a miniature tree. They have nothing to do with each other. Further, Bonzai is not a word at all - although it would make a great name for a calcium supplement for older people.
Reiki
靈氣 is the title of a healing practice now found globally but with origins in Japan.
Special note: Outside of the context of the healing practice of Reiki, this means “aura” or “spiritual essence that surrounds all living things.” A Japanese person unfamiliar with the practice will take the “aura” meaning.
Reiki is a technique for stress reduction and relaxation that also heals. It can be compared to massage but is based on the idea that an unseen “life force energy” flows through us and is what causes us to be alive. If your life force energy is low, you'll be more likely to get sick or feel stressed. If your life force energy is abundant and flowing well, you become more capable of being happy and healthy.
There is a lot of information available if you want to Google this term - my job is to offer the calligraphy while you can decide if it is right for you.
Note: We are showing the ancient (traditional) form of the Reiki Kanji. I have seen Reiki written with the slightly simplified version and this more classic form. If you want the form of Reiki with the two strokes in the shape of an X on the second character and the modern first character, simply click on the Kanji characters to the right.
Note: 靈氣 is also a Chinese word, but in Chinese, these characters create a word that refers to a smart person or someone with high aspirations. It is not read as a healing method in Chinese.
In Korean Hanja, this can be read as a “mysterious atmosphere” by a Korean who is not familiar with the practice of Reiki (still has a cool meaning in Korean).
Hapkido
Korean Martial Art of re-directing force
Hapkido or 合氣道 is a mostly-defensive martial art in Korea.
Hapkido has some connection to the Aikido of Japan. They are written with the same characters in both languages. However, it should be noted that the Korean Hanja characters shown here are the traditional Chinese form - but in modern Japan, the middle character was slightly simplified.
Note: You can consider this to be the older Japanese written form of Aikido. Titles on older books and signs about Aikido use this form.
The connection between Japanese Aikido and Korean Hapkido is muddled in history. The issue is probably due to the difficult relationship between the two countries around WWII. Many Koreans became virtual slaves to the Japanese during that period. After WWII, many things in Korea were disassociated from having any Japanese origin. The relationship has greatly mellowed out now.
Looking at the characters, the first means “union” or “harmony.”
The second character means “universal energy” or “spirit.”
The third means “way” or “method.”
One way to translate this into English is the “Harmonizing Energy Method.” This makes sense, as Hapkido has more to do with redirecting energy than fighting strength against strength.
More Hapkido info
More notes:
1. Sometimes Hapkido is Romanized as “hap ki do,” “hapki-do” “hab gi do” or “hapgido.”
2. Korean Hanja characters are actually Chinese characters that usually hold the same meaning in both languages. There was a time when these characters were the standard and only written form of Korean. The development of modern Korean Hangul characters is a somewhat recent event in the greater scope of history. There was a time when Chinese characters were the written form of many languages in places known in modern times as North Korea, South Korea, Japan, Vietnam, Singapore, Hong Kong, Taiwan, Mainland China, and a significant portion of Malaysia. Even today, more people in the world can read Chinese characters than English.
3. While these Korean Hanja characters can be pronounced in Chinese, this word is not well-known in China and is not considered part of the Chinese lexicon.
Guanxi
The Chinese Concept of Relationship and Exchange of Favors
The dictionary definition is:
Relations/relationship, to concern, to affect, to have to do with, or connection.
But there's more to it...
In China, the relationship that you have with certain people can open doors for you. Having guanxi with someone also means they would never defraud you but are honor-bound to treat you fairly (of course, this goes both ways). Sometimes it is suggested that guanxi is the exchange of favors. 關繫 / 関繫 / 關係 is more about having a relationship that allows you to ask for and expect favors without shame.
There is no concept in western culture that exactly matches guanxi, but perhaps having a social or professional network is similar.
Note that there are some variations common within Chinese, Japanese Kanji, and Korean Hanja for this word... Japanese tend to use a Chinese alternate form as shown to the right for
Japanese tend to use a Chinese alternate form as shown to the right for
the first character.
 There's also another alternate form of that first character (currently used as the official Simplified form in mainland China) which looks like the character shown to the right. It's basically the central radical of the alternate version shown above but without the “door radical” around it. In more free-flowing calligraphy styles, this version would be the likely choice for a calligrapher.
There's also another alternate form of that first character (currently used as the official Simplified form in mainland China) which looks like the character shown to the right. It's basically the central radical of the alternate version shown above but without the “door radical” around it. In more free-flowing calligraphy styles, this version would be the likely choice for a calligrapher.
![]() In Modern Japanese, they use the character shown to the right.
In Modern Japanese, they use the character shown to the right.
They also tend to use this same form in Korean Hanja (I've only checked this word in my Korean dictionary, but it has not been confirmed by a translator's review).
![]() If that was not confusing enough, there is another alternate form of that second character. See right.
If that was not confusing enough, there is another alternate form of that second character. See right.
An Asian calligrapher of any nationality may use these forms at their discretion. However, They would tend to stick to the most common form used in their respective languages.
If you have any preference on any of these issues, please give us a special note with your order, and we'll make sure it's done the way you want.
The following table may be helpful for those studying Chinese or Japanese...
| Title | Characters | Romaji (Romanized Japanese) | Various forms of Romanized Chinese | |
| Simplicity | 簡 简 | kan | jiǎn / jian3 / jian | chien |
| Smooth and Steady | 平穩 平稳 | heion | píng wěn / ping2 wen3 / ping wen / pingwen | p`ing wen / pingwen / ping wen |
| Physical Strength | 體力 体力 | tairyoku | tǐ lì / ti3 li4 / ti li / tili | t`i li / tili / ti li |
| Doctor | 醫生 医生 | yī shēng / yi1 sheng1 / yi sheng / yisheng | i sheng / isheng | |
| Qian | 乾 干 | ken | gān qián gan1 / qian2 gan / qian gan/qian | kan ch`ien kanchien kan chien |
| France | 法國 法国 | furansu | fà guó / fa4 guo2 / fa guo / faguo | fa kuo / fakuo |
| Shotokan | 鬆濤館 松涛館 | shou tou kan shoutoukan sho to kan | sōng tāo guǎn song1 tao1 guan3 song tao guan songtaoguan | sung t`ao kuan sungtaokuan sung tao kuan |
| Shotokan Karate-Do | 鬆濤館空手道 松涛館空手道 | shou tou kan kara te dou shoutoukankaratedou sho to kan kara te do | sōng tāo guǎn kōng shǒu dào song1 tao1 guan3 kong1 shou3 dao4 song tao guan kong shou dao songtaoguankongshoudao | sung t`ao kuan k`ung shou tao sungtaokuankungshoutao sung tao kuan kung shou tao |
| Sakuragi | 櫻木 | sakuragi sakuraki | ||
| Kaylee | 凱麗 凯丽 | kǎi lì / kai3 li4 / kai li / kaili | k`ai li / kaili / kai li | |
| France | 法國 法国 | furansu | fà guó / fa4 guo2 / fa guo / faguo | fa kuo / fakuo |
| English Briton Person from England | 英國人 英国人 | ei koku jin eikokujin | yīng guó rén ying1 guo2 ren2 ying guo ren yingguoren | ying kuo jen yingkuojen |
| Gemini Zodiac Symbol Sign | 雙子座 双子座 | futago-za | shuāng zǐ zuò shuang1 zi3 zuo4 shuang zi zuo shuangzizuo | shuang tzu tso shuangtzutso |
| Hitori | 独 | hitori / doku | dú / du2 / du | tu |
| Ford | 福特 | fú tè / fu2 te4 / fu te / fute | fu t`e / fute / fu te | |
| Honor | 名譽 名誉 | meiyo | míng yù / ming2 yu4 / ming yu / mingyu | ming yü / mingyü |
| Empire | 帝國 帝国 | teikoku | dì guó / di4 guo2 / di guo / diguo | ti kuo / tikuo |
| Gemini Zodiac Symbol Sign | 雙子座 双子座 | futago-za | shuāng zǐ zuò shuang1 zi3 zuo4 shuang zi zuo shuangzizuo | shuang tzu tso shuangtzutso |
| Mumonkan The Gateless Gate | 無門関 | mu mon kan / mumonkan | ||
| Navy SEALS | 海豹部隊 海豹部队 | hǎi bào bù duì hai3 bao4 bu4 dui4 hai bao bu dui haibaobudui | hai pao pu tui haipaoputui |
|
| Twins | 雙子 双子 | futago | ||
| Doctor | 醫師 医师 | i shi / ishi | yī shī / yi1 shi1 / yi shi / yishi | i shih / ishih |
| Serenity Tranquility | 靜穏 静穏 | seion | ||
| The Holy Trinity | 三位一體 三位一体 | sān wèi yì tǐ san1 wei4 yi4 ti3 san wei yi ti sanweiyiti | san wei i t`i sanweiiti san wei i ti |
|
| The Gateless Gate | 無門關 无门关 | mu mon kan / mumonkan | wú mén guān wu2 men2 guan1 wu men guan wumenguan | wu men kuan wumenkuan |
| Sesshin | 接心 | sesshin / seshin | jiē xīn / jie1 xin1 / jie xin / jiexin | chieh hsin / chiehhsin |
| Kingdom of Heaven | 天國 天国 | tengoku | tiān guó / tian1 guo2 / tian guo / tianguo | t`ien kuo / tienkuo / tien kuo |
| Seikaze | 静風/靜風 静风 | seikaze / seifuu seikaze / seifu | jìng fēng jing4 feng1 jing feng jingfeng | ching feng chingfeng |
| Manga | 漫画 | manga | màn huà / man4 hua4 / man hua / manhua | |
| Courtesy Etiquette | 礼儀 / 禮儀 礼仪 | rei gi / reigi | lǐ yì / li3 yi4 / li yi / liyi | li i / lii |
| Shakyamuni The Buddha | 釈迦 | sha ka / shaka | shì jiā / shi4 jia1 / shi jia / shijia | shih chia / shihchia |
| Aiki O'Kami | 合氣大神 合気大神 | aikiokami | ||
| Kindheartedness Benevolence Humanity | 仁德 | jintoku | rén dé / ren2 de2 / ren de / rende | jen te / jente |
| Opportunity | 機會 机会 | kikai | jī huì / ji1 hui4 / ji hui / jihui | chi hui / chihui |
| Courtesy Etiquette | 禮儀 礼仪 | lǐ yì / li3 yi4 / li yi / liyi | li i / lii | |
| Kingdom of Heaven | 天國 天国 | tengoku | tiān guó / tian1 guo2 / tian guo / tianguo | t`ien kuo / tienkuo / tien kuo |
| Shiatsu-Do | 指圧道 | shiatsudou / shiatsudo | ||
| Reincarnation (Buddhism) | 轉世 转世 | ten sei / tensei | zhuǎn shì zhuan3 shi4 zhuan shi zhuanshi | chuan shih chuanshih |
| Sushi | 壽司 寿司 | su shi / sushi | shòu sī / shou4 si1 / shou si / shousi | shou ssu / shoussu |
| Independent Spirit Independent Heart | 獨立心 独立心 | dokuritsushin | ||
| Respect | 禮 礼 | rei | lǐ / li3 / li | |
| Zen Chan Meditation | 禪 禅 | zen | chán / chan2 / chan | ch`an / chan |
| Tang Soo Do Tang Hand Way | 唐手道 | kara te do / karatedo | táng shǒu dào tang2 shou3 dao4 tang shou dao tangshoudao | t`ang shou tao tangshoutao tang shou tao |
| Banzai Wansui | 萬歲 万岁 | banzai / manzai | wàn suì / wan4 sui4 / wan sui / wansui | |
| Kyojitsu: Falsehood and Truth | 虚実 | kyo jitsu / kyojitsu | ||
| Taido | 躰道 | tai dou / taidou / tai do | ||
| Banzai | 万歲 / 萬歲 万岁 | banzai | wàn suì / wan4 sui4 / wan sui / wansui | |
| Reiki | 靈氣 灵气 霊気 | reiki | líng qì / ling2 qi4 / ling qi / lingqi | ling ch`i / lingchi / ling chi |
| Hapkido | 合氣道 合气道 | ai ki do / aikido | hé qì dào he2 qi4 dao4 he qi dao heqidao | ho ch`i tao hochitao ho chi tao |
| Guanxi | 關繫 / 関繫 / 關係 关系 / 関係 | kankei | guān xì / guan1 xi4 / guan xi / guanxi | kuan hsi / kuanhsi |
| In some entries above you will see that characters have different versions above and below a line. In these cases, the characters above the line are Traditional Chinese, while the ones below are Simplified Chinese. | ||||
Successful Chinese Character and Japanese Kanji calligraphy searches within the last few hours...





















































